Additive Intraocular Pressure-Lowering Effects of Ripasudil with Glaucoma Therapeutic Agents in Rabbits and Monkeys
- PMID: 28540083
- PMCID: PMC5429944
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/7079645
Additive Intraocular Pressure-Lowering Effects of Ripasudil with Glaucoma Therapeutic Agents in Rabbits and Monkeys
Abstract
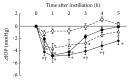
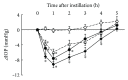
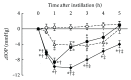
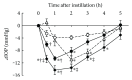
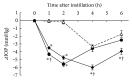
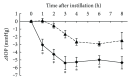
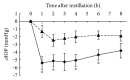
Ripasudil hydrochloride hydrate (K-115), a specific Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitor, is developed for the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Topical administration of ripasudil decreases intraocular pressure (IOP) by increasing conventional outflow through the trabeculae to Schlemm's canal, which is different from existing agents that suppress aqueous humor production or promote uveoscleral outflow. In this study, we demonstrated that ripasudil significantly lowered IOP in combined regimens with other glaucoma therapeutic agents in rabbits and monkeys. Ripasudil showed additional effects on maximum IOP lowering or prolonged the duration of IOP-lowering effects with combined administration of timolol, nipradilol, brimonidine, brinzolamide, latanoprost, latanoprost/timolol fixed combination, and dorzolamide/timolol fixed combination. These results indicate that facilitation of conventional outflow by ripasudil provides additive IOP-lowering effect with other classes of antiglaucoma agents. Ripasudil is expected to have substantial utility in combined regimens with existing agents for glaucoma treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Additive Intraocular Pressure-Lowering Effects of the Rho Kinase Inhibitor Ripasudil (K-115) Combined With Timolol or Latanoprost: A Report of 2 Randomized Clinical Trials.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015 Jul;133(7):755-61. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2015.0525. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25880207 Clinical Trial.
-
Ocular hypotensive effects of a Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor in rabbits.Clin Ophthalmol. 2017 Mar 31;11:591-597. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S131416. eCollection 2017. Clin Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28408797 Free PMC article.
-
Additive Intraocular Pressure-Lowering Effects of a Novel Selective EP2 Receptor Agonist, Omidenepag Isopropyl, Combined with Existing Antiglaucoma Agents in Conscious Ocular Normotensive Monkeys.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2021 May;37(4):223-229. doi: 10.1089/jop.2020.0071. Epub 2021 Feb 17. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33600237
-
Ripasudil hydrochloride hydrate: targeting Rho kinase in the treatment of glaucoma.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017 Oct;18(15):1669-1673. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2017.1378344. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28893104 Review.
-
Ripasudil Hydrochloride Hydrate in the Treatment of Glaucoma: Safety, Efficacy, and Patient Selection.Clin Ophthalmol. 2020 May 6;14:1229-1236. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S216907. eCollection 2020. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32440089 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ripasudil as a Potential Therapeutic Agent in Treating Secondary Glaucoma in HTLV-1-Uveitis: An In Vitro Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 12;25(6):3229. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063229. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542203 Free PMC article.
-
Rho Kinase Inhibitors: Strategies in Glaucoma Treatment in Older Adults.Drugs Aging. 2024 May;41(5):399-406. doi: 10.1007/s40266-024-01107-y. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Drugs Aging. 2024. PMID: 38416395 Review.
-
Effects of Lentivirus-Mediated C3 Expression on Trabecular Meshwork Cells and Intraocular Pressure.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Oct 1;59(12):4937-4944. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-24978. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30326062 Free PMC article.
-
Rho kinase inhibitor for primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 10;6(6):CD013817. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013817.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35686679 Free PMC article.
-
Rho Kinase Inhibitor AR-12286 Reverses Steroid-Induced Changes in Intraocular Pressure, Effective Filtration Areas, and Morphology in Mouse Eyes.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Feb 1;64(2):7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.2.7. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 36734964 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

