Orthodontic Intervention to Impacted and Transposed Lower Canines
- PMID: 28540090
- PMCID: PMC5429916
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/4105713
Orthodontic Intervention to Impacted and Transposed Lower Canines
Abstract
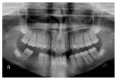
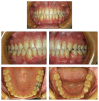
Impacted and transposed teeth cause serious difficulties in tooth eruption and movement as well as esthetic and functional outcomes. Proper treatment planning including good biomechanical control is essential in order to avoid side effects during traction and aligning of the impacted and/or transposed teeth. The purpose of the present study was to present a successfully treated female patient having transposed and impacted lower canines by means of a modified lingual arch and fixed orthodontic appliance. A female patient aged 13 years and 9 months presented to the orthodontic department with a chief compliant of bilateral spacing and missing teeth in mandibular dentition. After leveling and creating sufficient space in the mandibular arch for the canines, a modified lingual arch was cemented to the mandibular first molars. The lingual arch had two hooks extending to the distobuccal areas of the canine spaces. Elastic chains were applied between the hooks on the lingual arch and the ligatures tied to the attachments on the canine crowns. The light forces generated by elastic materials caused impacted canines to erupt and tend towards their own spaces in the dental arch. As a result, impacted and transposed lower canines were properly positioned in their spaces, and the treatment results were stable during the retention period.
Figures




References
-
- Daskalogiannakis J. Glossary of Orthodontic Terms. 1st. Berlin, Germany: Quintessence Publishing; 2000.
-
- Yavuz M. S., Aras M. H., Büyükkurt M. C., Tozoglu S. Impacted mandibular canines. Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice. 2007;8:78–85. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

