Inhibition of protein kinases by anticancer DNA intercalator, 4-butylaminopyrimido[4',5':4,5]thieno(2,3- b)quinoline
- PMID: 28540166
- PMCID: PMC5430831
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2017.01.001
Inhibition of protein kinases by anticancer DNA intercalator, 4-butylaminopyrimido[4',5':4,5]thieno(2,3- b)quinoline
Abstract
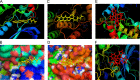
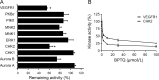
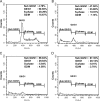
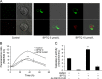
Targeting protein kinases (PKs) has been a promising strategy in treating cancer, as PKs are key regulators of cell survival and proliferation. Here in this study, we studied the ability of pyrimido[4',5':4,5]thieno(2,3-b)quinolines (PTQ) to inhibit different PKs by performing computational docking and in vitro screening. Docking studies revealed that 4-butylaminopyrimido[4',5':4,5]thieno(2,3-b)quinoline (BPTQ) has a higher order of interaction with the kinase receptors than other PTQ derivatives. In vitro screening confirms that BPTQ inhibits VEGFR1 and CHK2, with the IC50 values of 0.54 and 1.70 µmol/L, respectively. Further, cytotoxicity of BPTQ was measured by trypan blue assay. Treatment with BPTQ decreased the proliferation of HL-60 cells with an IC50 value of 12 µmol/L and induces apoptosis, as explicated by the fall in the mitochondrial membrane potential, annexin V labeling and increased expression of caspase-3. Taken together, these data suggest that BPTQ possess ability to inhibit PKs and to induce cell death in human promyelocytic leukemia cells.
Keywords: Anticancer drugs; Apoptosis; Chemotherapy; DNA intercalator; Kinase inhibitor; Molecular docking.
Figures

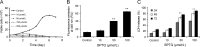
Similar articles
-
DNA intercalative 4-butylaminopyrimido[4',5':4,5]thieno(2,3-b)quinoline induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in leukemia cells.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;75(6):1121-33. doi: 10.1007/s00280-015-2735-6. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25819915
-
Intercalative pyrimido[4',5':4,5]thieno(2,3-b)quinolines induce apoptosis in leukemic cells: a comparative study of methoxy and morpholino substitution.Invest New Drugs. 2011 Oct;29(5):873-82. doi: 10.1007/s10637-010-9436-0. Epub 2010 Apr 28. Invest New Drugs. 2011. PMID: 20424886
-
Synthesis, DNA binding and cytotoxic activity of pyrimido[4',5':4,5]thieno(2,3-b)quinoline with 9-hydroxy-4-(3-diethylaminopropylamino) and 8-methoxy-4-(3-diethylaminopropylamino) substitutions.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018 Jan;178:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.10.022. Epub 2017 Nov 1. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018. PMID: 29101867
-
Genotoxicity of DNA Intercalating Anticancer Drugs: Pyrimido[4(I),5(I):4,5] thieno(2,3-b)quinolines on Somatic and Germinal Cells.Toxicol Mech Methods. 2007;17(3):135-45. doi: 10.1080/15376510600899605. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2007. PMID: 20020962
-
8-Methyl-4-(3-diethylaminopropylamino) pyrimido [4',5';4,5] thieno (2,3-b) quinoline (MDPTQ), a quinoline derivate that causes ROS-mediated apoptosis in leukemia cell lines.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007 Jul 1;222(1):80-8. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2007.04.005. Epub 2007 May 4. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17553538
References
-
- Robison K. Application of second-generation sequencing to cancer genomics. Brief Bioinform. 2010;11:524–534. - PubMed
-
- Shahabuddin M.S., Nambiar M., Choudhary B., Advirao G.M., Raghavan S.C. A novel DNA intercalator, butylamino-pyrimido[4′,5′:4,5]selenolo(2,3-b)quinoline, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in leukemic cells. Invest New Drugs. 2010;28:35–48. - PubMed
-
- Pearson M.A., Fabbro D. Targeting protein kinases in cancer therapy: a success? Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2004;4:1113–1124. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

