Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 5 is Required for Low-Concentration H2O2-Induced Angiogenesis of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 28540300
- PMCID: PMC5429924
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/6895730
Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 5 is Required for Low-Concentration H2O2-Induced Angiogenesis of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Abstract
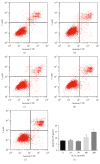
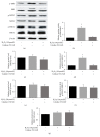
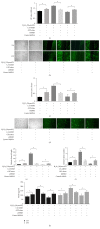
Background. The aim of this study was to assess the effects of low concentrations of H2O2 on angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in vitro and explore the underlying mechanisms. Methods. HUVECs were cultured and stimulated with different concentrations of H2O2. Flow cytometric analysis was used to select an optimal concentration of H2O2 for the following experiments. Cell proliferation, migration, and tubule formation were evaluated by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assays, scratch wound assays, and Matrigel tubule formation assays, respectively. For gain and loss of function studies, constitutively active MEK5 (CA-MEK5) and ERK5 shRNA lentiviruses were used to activate or knock down extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5). Results. We found that low concentrations of H2O2 promoted HUVECs proliferation, migration, and tubule formation. ERK5 in HUVECs was significantly activated by H2O2. Enhanced ERK5 activity significantly amplified the proangiogenic effects of H2O2; in contrast, ERK5 knock-down abrogated the effects of H2O2. Conclusions. Our results confirmed that low concentrations of H2O2 promoted HUVECs angiogenesis in vitro, and ERK5 is an essential mediator of this process. Therefore, ERK5 may be a potential therapeutic target for promoting angiogenesis and improving graft survival.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Erk5 inhibits endothelial migration via KLF2-dependent down-regulation of PAK1.Cardiovasc Res. 2015 Jan 1;105(1):86-95. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu236. Epub 2014 Nov 10. Cardiovasc Res. 2015. PMID: 25388666
-
Cryptotanshinone inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis by targeting the VEGFR2 signaling pathway.Microvasc Res. 2017 May;111:25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2016.12.011. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Microvasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28040437
-
Pro-angiogenic activity of notoginsenoside R1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro and in a chemical-induced blood vessel loss model of zebrafish in vivo.Chin J Integr Med. 2016 Jun;22(6):420-9. doi: 10.1007/s11655-014-1954-8. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Chin J Integr Med. 2016. PMID: 25533511
-
ERK5 and its role in tumour development.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Feb;40(1):251-6. doi: 10.1042/BST20110663. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22260700 Review.
-
Pathophysiological Impact of the MEK5/ERK5 Pathway in Oxidative Stress.Cells. 2023 Apr 13;12(8):1154. doi: 10.3390/cells12081154. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37190064 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reactive Oxygen Species and Endothelial Ca2+ Signaling: Brothers in Arms or Partners in Crime?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 10;22(18):9821. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189821. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WNK lysine deficient protein kinase 1 regulates human endometrial stromal cell decidualization, proliferation, and migration in part through mitogen-activated protein kinase 7.Biol Reprod. 2017 Sep 1;97(3):400-412. doi: 10.1093/biolre/iox108. Biol Reprod. 2017. PMID: 29025069 Free PMC article.
-
KRIT1: A Traffic Warden at the Busy Crossroads Between Redox Signaling and the Pathogenesis of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Mar;38(7-9):496-528. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0263. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 36047808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kurzyk A. Angiogenesis—possibilities, problems and perspectives. Postepy Biochemii. 2015;61(1):25–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

