Development of a hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometric imaging platform for N-glycan relative quantitation using stable-isotope labeled hydrazide reagents
- PMID: 28540462
- PMCID: PMC6822905
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-017-0387-6
Development of a hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometric imaging platform for N-glycan relative quantitation using stable-isotope labeled hydrazide reagents
Abstract
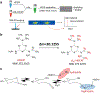
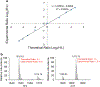
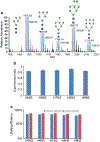
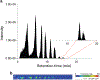
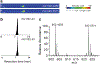
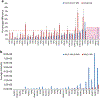
In this work, the capability of newly developed hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) coupled with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometric imaging (MALDI-MSI) platform for quantitative analysis of N-glycans has been demonstrated. As a proof-of-principle experiment, heavy and light stable-isotope labeled hydrazide reagents labeled maltodextrin ladder were used to demonstrate the feasibility of the HILIC-MALDI-MSI platform for reliable quantitative analysis of N-glycans. MALDI-MSI analysis by an Orbitrap mass spectrometer enabled high-resolution and high-sensitivity detection of N-glycans eluted from HILIC column, allowing the re-construction of LC chromatograms as well as accurate mass measurements for structural inference. MALDI-MSI analysis of the collected LC traces showed that the chromatographic resolution was preserved. The N-glycans released from human serum was used to demonstrate the utility of this novel platform in quantitative analysis of N-glycans from a complex sample. Benefiting from the minimized ion suppression provided by HILIC separation, comparison between MALDI-MS and the newly developed platform HILIC-MALDI-MSI revealed that HILIC-MALDI-MSI provided higher N-glycan coverage as well as better quantitation accuracy in the quantitative analysis of N-glycans released from human serum. Graphical abstract Reconstructed chromatograms based on HILIC-MALDI-MSI results of heavy and light labeled maltodextrin enabling quantitative glycan analysis.
Keywords: Glycomics; HILIC; Hydrazide reagents; MALDI imaging; N-Glycans; Quantitation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liquid chromatography-matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric imaging with sprayed matrix for improved sensitivity, reproducibility and quantitation.Analyst. 2013 Nov 7;138(21):6600-6. doi: 10.1039/c3an01225e. Analyst. 2013. PMID: 24003441 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid sample preparation method for mass spectrometric characterization of N-linked glycans.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2005;19(16):2331-6. doi: 10.1002/rcm.2067. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2005. PMID: 16041822
-
Sensitive and robust MALDI-TOF-MS glycomics analysis enabled by Girard's reagent T on-target derivatization (GTOD) of reducing glycans.Anal Chim Acta. 2019 Feb 7;1048:105-114. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.10.015. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Anal Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 30598139 Free PMC article.
-
[Applications of chromatography in glycomics].Se Pu. 2024 Jul;42(7):646-657. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2023.12003. Se Pu. 2024. PMID: 38966973 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging of N-Linked Glycans in Tissues.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1104:59-76. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-2158-0_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30484244 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Analytical Approaches for Glycan and Glycopeptide Quantitation.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2021;20:100054. doi: 10.1074/mcp.R120.002095. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 32576592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-specific characterization and quantitation of N-glycopeptides in PKM2 knockout breast cancer cells using DiLeu isobaric tags enabled by electron-transfer/higher-energy collision dissociation (EThcD).Analyst. 2018 May 29;143(11):2508-2519. doi: 10.1039/c8an00216a. Analyst. 2018. PMID: 29687791 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Membrane N-Glycoproteomics Using Human Breast Cancer Cell Line Pairs.Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2023;12(1):A0117. doi: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0117. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2023. PMID: 37250596 Free PMC article.
-
ADVANCES IN HIGH-RESOLUTION MALDI MASS SPECTROMETRY FOR NEUROBIOLOGY.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2022 Mar;41(2):194-214. doi: 10.1002/mas.21661. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2022. PMID: 33165982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass spectrometry in clinical glycomics: The path from biomarker identification to clinical implementation.Clin Mass Spectrom. 2020 Aug 27;18:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.clinms.2020.08.001. eCollection 2020 Nov. Clin Mass Spectrom. 2020. PMID: 34820521 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ohtsubo K, Marth JD. Glycosylation in cellular mechanisms of health and disease. Cell. 2006;126(5):855–67. - PubMed
-
- Apweiler R, Hermjakob H, Sharon N. On the frequency of protein glycosylation, as deduced from analysis of the SWISS-PROT database. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Gen Subj. 1999;1473(1):4–8. - PubMed
-
- Jaeken J. Congenital disorders of glycosylation. Ann N YAcad Sci. 2010;1214(1):190–8. - PubMed
-
- Fuster MM, Esko JD. The sweet and sour of cancer: glycans as novel therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(7):526–42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

