Development of a hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometric imaging platform for N-glycan relative quantitation using stable-isotope labeled hydrazide reagents
- PMID: 28540462
- PMCID: PMC6822905
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-017-0387-6
Development of a hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometric imaging platform for N-glycan relative quantitation using stable-isotope labeled hydrazide reagents
Abstract
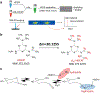
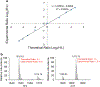
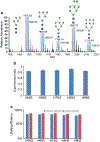
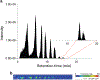
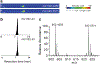
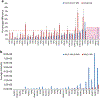
In this work, the capability of newly developed hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) coupled with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometric imaging (MALDI-MSI) platform for quantitative analysis of N-glycans has been demonstrated. As a proof-of-principle experiment, heavy and light stable-isotope labeled hydrazide reagents labeled maltodextrin ladder were used to demonstrate the feasibility of the HILIC-MALDI-MSI platform for reliable quantitative analysis of N-glycans. MALDI-MSI analysis by an Orbitrap mass spectrometer enabled high-resolution and high-sensitivity detection of N-glycans eluted from HILIC column, allowing the re-construction of LC chromatograms as well as accurate mass measurements for structural inference. MALDI-MSI analysis of the collected LC traces showed that the chromatographic resolution was preserved. The N-glycans released from human serum was used to demonstrate the utility of this novel platform in quantitative analysis of N-glycans from a complex sample. Benefiting from the minimized ion suppression provided by HILIC separation, comparison between MALDI-MS and the newly developed platform HILIC-MALDI-MSI revealed that HILIC-MALDI-MSI provided higher N-glycan coverage as well as better quantitation accuracy in the quantitative analysis of N-glycans released from human serum. Graphical abstract Reconstructed chromatograms based on HILIC-MALDI-MSI results of heavy and light labeled maltodextrin enabling quantitative glycan analysis.
Keywords: Glycomics; HILIC; Hydrazide reagents; MALDI imaging; N-Glycans; Quantitation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ohtsubo K, Marth JD. Glycosylation in cellular mechanisms of health and disease. Cell. 2006;126(5):855–67. - PubMed
-
- Apweiler R, Hermjakob H, Sharon N. On the frequency of protein glycosylation, as deduced from analysis of the SWISS-PROT database. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Gen Subj. 1999;1473(1):4–8. - PubMed
-
- Jaeken J. Congenital disorders of glycosylation. Ann N YAcad Sci. 2010;1214(1):190–8. - PubMed
-
- Fuster MM, Esko JD. The sweet and sour of cancer: glycans as novel therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(7):526–42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

