Effect of Early Plasma Exchange on Survival in Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome: A Multicenter Study
- PMID: 28541003
- PMCID: PMC5447121
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.4.867
Effect of Early Plasma Exchange on Survival in Patients with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome: A Multicenter Study
Abstract
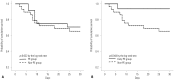
Despite a high mortality rate, no specific treatment for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) has been established. This study compared the clinical outcomes of SFTS patients treated with plasma exchange (PE group) with those who were not treated (non-PE group) at nine Korean hospitals between May 2013 and August 2015. A total of 53 SFTS patients were included: 24 (45.3%) PE cases and 29 (54.7%) non-PE cases. The overall in-hospital mortality rate was 32.1% (17/53). The in-hospital mortality rate of the PE group did not differ from that of the non-PE group (29.3% vs. 34.5%, p=0.680). Of the 24 PE cases, 16 (66.7%) were treated with PE within 7 days of symptom onset (early PE group). The early PE group survived longer than the non-PE group (mean 28.4 days vs. 22.6 days, p=0.044). Multivariate analysis showed an inverse association between early PE implementation and 30-day mortality (adjusted hazard ratio 0.052, 95% confidence interval 0.004-0.678, p=0.024). The results of this study suggest that early PE implementation may have a beneficial effect on the clinical outcome of SFTS patients.
Keywords: Phlebovirus; Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome; plasma exchange; treatment.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2017.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Li DX. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: a newly discovered emerging infectious disease. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015;21:614–620. - PubMed
-
- Liu Q, He B, Huang SY, Wei F, Zhu XQ. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, an emerging tick-borne zoonosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:763–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

