Combination Steroid and Test-based Food Elimination for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Retrospective Analysis
- PMID: 28541260
- PMCID: PMC5432094
- DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001584
Combination Steroid and Test-based Food Elimination for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a clinicopathologic disorder characterized by infiltration of eosinophils into the esophagus. Primary treatment approaches include topical corticosteroids and/or food elimination. The aim of the present study was to compare the effectiveness of combination therapy (topical corticosteroid plus test-based food elimination [FS]) with single therapy (topical corticosteroid [S] or test-based food elimination [F]).
Methods: Chart review of patients with EoE at Texas Children's Hospital (age <21 years) was performed. Clinical and histological statuses were evaluated after a 3-month treatment with either single or combination therapy. Comparisons were analyzed using Fisher exact test, Kruskal-Wallis tests, and multiple logistic regression models.
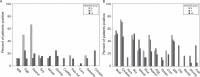
Results: Among 670 charts, 63 patients (1-21 years, median 10.3 years) with clinicopathologic diagnoses of EoE were identified. Combination FS therapy was provided to 51% (n = 32) and single treatment (S, F) to 27% (n = 17) or 22% (n = 14) of patients, respectively. Clinical responses were noted in 91% (n = 29), 71% (n = 12), and 64% (n = 14) of patients in the FS, S, and F groups, respectively. The odds of clinically improving were 4.6 times greater (95% confidence interval: 1.1-18.8) with combination versus single therapy. The median peak number of eosinophils per high-power field after 3-month therapy was not significantly different in the S, F, and FS groups.
Conclusions: The combination of topical corticosteroids with specific food elimination is as effective in achieving clinical and histological remissions as the single-treatment approaches. Responses were achieved with the combination in patients who had previously failed single-agent therapy. Prospective research of this combination approach in young patients with EoE is needed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combined and Alternating Topical Steroids and Food Elimination Diet for the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Sep;63(9):2381-2388. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-4931-9. Epub 2018 Jan 29. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29380175 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective, comparative effectiveness trial of cow's milk elimination and swallowed fluticasone for pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis.Dis Esophagus. 2016 May;29(4):377-84. doi: 10.1111/dote.12339. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Dis Esophagus. 2016. PMID: 25721813
-
Efficacy of a 4-Food Elimination Diet for Children With Eosinophilic Esophagitis.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Nov;15(11):1698-1707.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.05.048. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28603055 Free PMC article.
-
Model to Determine the Optimal Dietary Elimination Strategy for Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Nov;16(11):1730-1737.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.04.013. Epub 2018 May 3. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29730438
-
Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis in the pediatric patient: an evidence-based approach.Eur J Pediatr. 2018 May;177(5):649-663. doi: 10.1007/s00431-018-3129-7. Epub 2018 Mar 17. Eur J Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29549437 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Dietary Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Children and Adults: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 11;16(14):2231. doi: 10.3390/nu16142231. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064673 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis in children: doubts and future perspectives.J Transl Med. 2019 Aug 9;17(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-2014-0. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31399124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technical Review on the Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Report From the AGA Institute and the Joint Task Force on Allergy-Immunology Practice Parameters.Gastroenterology. 2020 May;158(6):1789-1810.e15. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.039. Gastroenterology. 2020. PMID: 32359563 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Food Elimination Diet for Eosinophilic Esophagitis Refractory to Monotherapy.Gastro Hep Adv. 2022 Apr 14;1(4):596-600. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2022.04.002. eCollection 2022. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022. PMID: 39132073 Free PMC article.
-
Combined and Alternating Topical Steroids and Food Elimination Diet for the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Sep;63(9):2381-2388. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-4931-9. Epub 2018 Jan 29. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29380175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011; 128:3.e6–20.e6. - PubMed
-
- Soon IS, Butzner JD, Kaplan GG, et al. Incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2013; 57:72–80. - PubMed
-
- Aceves SS, Newbury RO, Dohil R, et al. Esophageal remodeling in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 119:206–212. - PubMed
-
- Lucendo AJ, Castillo P, Martin-Chavarri S, et al. Manometric findings in adult eosinophilic oesophagitis: a study of 12 cases. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007; 19:417–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

