Hypoxia as a target for drug combination therapy of liver cancer
- PMID: 28542038
- PMCID: PMC5515631
- DOI: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000516
Hypoxia as a target for drug combination therapy of liver cancer
Abstract
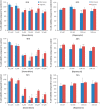
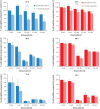
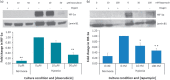
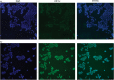
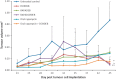
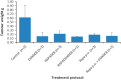
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third most frequent cause of cancer deaths worldwide. The standard of care for intermediate HCC is transarterial chemoembolization, which combines tumour embolization with locoregional delivery of the chemotherapeutic doxorubicin. Embolization therapies induce hypoxia, leading to the escape and proliferation of hypoxia-adapted cancer cells. The transcription factor that orchestrates responses to hypoxia is hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1). The aim of this work is to show that targeting HIF-1 with combined drug therapy presents an opportunity for improving outcomes for HCC treatment. HepG2 cells were cultured under normoxic and hypoxic conditions exposed to doxorubicin, rapamycin and combinations thereof, and analyzed for viability and the expression of hypoxia-induced HIF-1α in response to these treatments. A pilot study was carried out to evaluate the antitumour effects of these drug combinations delivered from drug-eluting beads in vivo using an ectopic xenograft murine model of HCC. A therapeutic doxorubicin concentration that inhibits the viability of normoxic and hypoxic HepG2 cells and above which hypoxic cells are chemoresistant was identified, together with the lowest effective dose of rapamycin against normoxic and hypoxic HepG2 cells. It was shown that combinations of rapamycin and doxorubicin are more effective than doxorubicin alone. Western Blotting indicated that both doxorubicin and rapamycin inhibit hypoxia-induced accumulation of HIF-1α. Combination treatments were more effective in vivo than either treatment alone. mTOR inhibition can improve outcomes of doxorubicin treatment in HCC.
Figures
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 2005; 55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Sala M, Llovet JM. Chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2004; 127 (Suppl 1):S179–S188. - PubMed
-
- Ackerman NB. Experimental studies on the circulation dynamics of intrahepatic tumor blood supply. Cancer 1972; 29:435–439. - PubMed
-
- Varela M, Real MI, Burrel M, Forner A, Sala M, Brunet M, et al. Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with drug eluting beads: efficacy and doxorubicin pharmacokinetics. J Hepatol 2007; 46:474–481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

