Current Tobacco Smoking and Desire to Quit Smoking Among Students Aged 13-15 Years - Global Youth Tobacco Survey, 61 Countries, 2012-2015
- PMID: 28542119
- PMCID: PMC5657874
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6620a3
Current Tobacco Smoking and Desire to Quit Smoking Among Students Aged 13-15 Years - Global Youth Tobacco Survey, 61 Countries, 2012-2015
Abstract
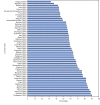
Tobacco use is the world's leading cause of preventable morbidity and mortality, resulting in nearly 6 million deaths each year (1). Smoked tobacco products, such as cigarettes and cigars, are the most common form of tobacco consumed worldwide (2), and most tobacco smokers begin smoking during adolescence (3). The health benefits of quitting are greater for persons who stop smoking at earlier ages; however, quitting smoking at any age has health benefits (4). CDC used the Global Youth Tobacco Survey (GYTS) data from 61 countries across the six World Health Organization (WHO) regions from 2012 to 2015 to examine the prevalence of current tobacco smoking and desire to quit smoking among students aged 13-15 years. Across all 61 countries, the median current tobacco smoking prevalence among students aged 13-15 years was 10.7% (range = 1.7%, Sri Lanka to 35.0%, Timor-Leste). By sex, the median current tobacco smoking prevalence was 14.6% among males (range = 2.9%, Tajikistan to 61.4%, Timor-Leste) and 7.5% among females (range = 1.6%, Tajikistan to 29.0%, Bulgaria). In the majority of countries assessed, the proportion of current tobacco smokers who desired to quit smoking exceeded 50%. These findings could be used by country level tobacco control programs to inform strategies to prevent and reduce youth tobacco use (1,4).
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO global report: mortality attributable to tobacco. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2012. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44815/1/9789241564434_eng.pdf
-
- CDC Foundation. Global Adult Tobacco Survey atlas. Atlanta, GA: CDC Foundation; 2015. http://gatsatlas.org/
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Preventing tobacco use among youth and young adults: a report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion; 2012. https://www.surgeongeneral.gov/library/reports/preventing-youth-tobacco-...
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services. The health consequences of smoking—50 years of progress: a report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking Health; 2014. https://www.surgeongeneral.gov/library/reports/50-years-of-progress/full...
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2005. http://www.who.int/tobacco/framework/WHO_FCTC_english.pdf
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

