Effect of combined actions of hip adduction/abduction on the force generation and maintenance of pelvic floor muscles in healthy women
- PMID: 28542276
- PMCID: PMC5443498
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177575
Effect of combined actions of hip adduction/abduction on the force generation and maintenance of pelvic floor muscles in healthy women
Abstract
Pelvic floor muscle (PFM) force and coordination are related to urinary incontinence severity and to sexual satisfaction. Health professionals frequently combine classic PFM exercises with hip adduction/abduction contraction to treat these disorders, but the real benefits of this practice are still unknown. Based on a theoretical anatomy approach whereby the levator ani muscle is inserted into the obturator internus myofascia and in which force generated by hip movements should increase the contraction quality of PFMs, our aim was to investigate the effects of isometric hip adduction and abduction on PFM force generation. Twenty healthy, nulliparous women were evaluated using two strain-gauge dynamometers (one cylinder-like inside the vaginal cavity, and the other measuring hip adduction/abduction forces around both thighs) while performing three different tasks: (a) isolated PFM contraction; (b) PFM contraction combined with hip adduction (30% and 50% maximum hip force); and (c) PFM contraction combined with hip abduction (30% and 50% maximum hip force). Data were sampled at 100Hz and subtracted from the offset if existent. We calculated a gradient between the isolated PFM contraction and each hip condition (Δ Adduction and Δ Abduction) for all variables: Maximum force (N), instant of maximum-force occurrence (s), mean force in an 8-second window (N), and PFM force loss (N.s). We compared both conditions gradients in 30% and 50% by paired t-tests. All variables did not differ between hip conditions both in 30% and 50% of maximum hip force (p>.05). PFM contraction combined with isometric hip abduction did not increase vaginal force in healthy and nulliparous women compared to PFM contraction combined with isometric hip adduction. Therefore, so far, the use of hip adduction or abduction in PFM training and treatments are not justified for improving PFM strength and endurance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

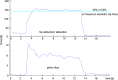
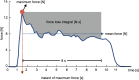
References
-
- Kepenekci I, Keskinkilic B, Akinsu F, Cakir P, Elhan AH, Erkek AB, et al. Prevalence of pelvic floor disorders in the female population and the impact of age, mode of delivery, and parity. Dis Colon Rectum. 2011;54: 85–94. doi: 10.1007/DCR.0b013e3181fd2356 - DOI - PubMed
-
- DeLancey JOL, Ashton-Miller JA. Pathophysiology of adult urinary incontinence. Gastroenterology. 2004;126: S23–S32. - PubMed
-
- Madill SJ, Harvey MA, McLean L. Women with stress urinary incontinence demonstrate motor control differences during coughing. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2010;20: 804–812. doi: 10.1016/j.jelekin.2009.10.006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Morin M, Bourbonnais D, Gravel D, Dumoulin C, Lemieux MC. Pelvic floor muscle function in continent and stress urinary incontinent women using dynamometric measurements. Neurourol Urodyn. 2004;23: 668–674. doi: 10.1002/nau.20069 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dietz HP, Steensma AB. The prevalence of major abnormalities of the levator ani in urogynaecological patients. BJOG An Int J Obstet Gynaecol. 2006;113: 225–230. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

