Oligopeptides as full-length New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1 (NDM-1) inhibitors
- PMID: 28542279
- PMCID: PMC5441612
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177293
Oligopeptides as full-length New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1 (NDM-1) inhibitors
Abstract
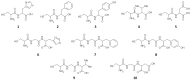
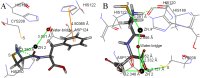
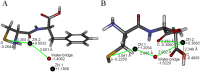
'Superbug' bacteria producing NDM-1 enzyme causing wide public concern were first detected in a patient who visited India in 2008. It's an effective approach to combining β-lactam antibiotics with NDM-1 inhibitor for treating NDM-1 producing strain infection. In our research, we designed ten oligopeptides, tested IC50 values against NDM-1 enzyme, determined the MIC values of synergistic antibacterial effect and explored the binding model. We found that the oligopeptides 2 (Cys-Phe) and 5 (Cys-Asp) respectively presented IC50 values of 113 μM and 68 μM and also displayed favorable synergistic effects of the inhibitors in combination with ertapenem against genetic engineering-host E. coli BL21 (DE3)/pET30a-NDM-1 and a clinical isolate of P. aeruginosa with blaNDM-1. Flexible docking and partial charge study suggested the interaction between oligopeptide and NDM-1. Three types of action effects, hydrogen bond, electrostatic effect and π-π interaction, contributed to the inhibitory activities.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Giedraitienė A, Vitkauskienė A, Naginienė R, Pavilonis A. Antibiotic resistance mechanisms of clinically important bacteria. Medicina (Kaunas). 2011; 47: 137–146. - PubMed
-
- Wickens H, Wade P. Understanding antibiotic resistance. Pharmaceutical journal 2005; 274: 501–504.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

