In vivo and in vitro characterization of DdrC, a DNA damage response protein in Deinococcus radiodurans bacterium
- PMID: 28542368
- PMCID: PMC5436757
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177751
In vivo and in vitro characterization of DdrC, a DNA damage response protein in Deinococcus radiodurans bacterium
Abstract
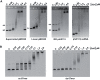
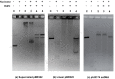
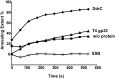
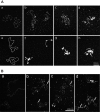
The bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans possesses a set of Deinococcus-specific genes highly induced after DNA damage. Among them, ddrC (dr0003) was recently re-annotated, found to be in the inverse orientation and called A2G07_00380. Here, we report the first in vivo and in vitro characterization of the corrected DdrC protein to better understand its function in irradiated cells. In vivo, the ΔddrC null mutant is sensitive to high doses of UV radiation and the ddrC deletion significantly increases UV-sensitivity of ΔuvrA or ΔuvsE mutant strains. We show that the expression of the DdrC protein is induced after γ-irradiation and is under the control of the regulators, DdrO and IrrE. DdrC is rapidly recruited into the nucleoid of the irradiated cells. In vitro, we show that DdrC is able to bind single- and double-stranded DNA with a preference for the single-stranded DNA but without sequence or shape specificity and protects DNA from various nuclease attacks. DdrC also condenses DNA and promotes circularization of linear DNA. Finally, we show that the purified protein exhibits a DNA strand annealing activity. Altogether, our results suggest that DdrC is a new DNA binding protein with pleiotropic activities. It might maintain the damaged DNA fragments end to end, thus limiting their dispersion and extensive degradation after exposure to ionizing radiation. DdrC might also be an accessory protein that participates in a single strand annealing pathway whose importance in DNA repair becomes apparent when DNA is heavily damaged.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural and functional characterization of DdrC, a novel DNA damage-induced nucleoid associated protein involved in DNA compaction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jul 22;50(13):7680-7696. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac563. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35801857 Free PMC article.
-
The deinococcal DdrB protein is involved in an early step of DNA double strand break repair and in plasmid transformation through its single-strand annealing activity.DNA Repair (Amst). 2011 Dec 10;10(12):1223-31. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.09.010. Epub 2011 Oct 2. DNA Repair (Amst). 2011. PMID: 21968057 Free PMC article.
-
DdrC, a unique DNA repair factor from D. radiodurans, senses and stabilizes DNA breaks through a novel lesion-recognition mechanism.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Aug 27;52(15):9282-9302. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae635. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39036966 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant defense of Deinococcus radiodurans: how does it contribute to extreme radiation resistance?Int J Radiat Biol. 2023;99(12):1803-1829. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2023.2241895. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Int J Radiat Biol. 2023. PMID: 37498212 Review.
-
Coexistence of SOS-Dependent and SOS-Independent Regulation of DNA Repair Genes in Radiation-Resistant Deinococcus Bacteria.Cells. 2021 Apr 16;10(4):924. doi: 10.3390/cells10040924. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33923690 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The DR2416/DR2415 two-component system is responsible for the radioresistance of Deinococcus radiodurans.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025 Jul 18;118(9):116. doi: 10.1007/s10482-025-02125-5. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025. PMID: 40679538
-
DdrI, a cAMP Receptor Protein Family Member, Acts as a Major Regulator for Adaptation of Deinococcus radiodurans to Various Stresses.J Bacteriol. 2018 Jun 11;200(13):e00129-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00129-18. Print 2018 Jul 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29686138 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptomics reveal a novel tardigrade-specific DNA-binding protein induced in response to ionizing radiation.Elife. 2024 Jul 9;13:RP92621. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92621. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38980300 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-induced nucleoid remodeling in Deinococcus radiodurans is associated with major changes in Heat Unstable (HU) protein dynamics.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jun 24;52(11):6406-6423. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae379. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38742631 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Radiation Desiccation Response Regulon of the Radioresistant Bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans by Integrative Genomic Analyses.Cells. 2021 Sep 25;10(10):2536. doi: 10.3390/cells10102536. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blasius M, Sommer S, Hubscher U (2008) Deinococcus radiodurans: what belongs to the survival kit? Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 43: 221–238. doi: 10.1080/10409230802122274 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Confalonieri F, Sommer S (2011) Bacterial and archaeal resistance to ionizing radiation. J Phys:ConfSer 261:
-
- Daly MJ (2009) A new perspective on radiation resistance based on Deinococcus radiodurans. Nat Rev Microbiol 7: 237–245. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2073 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ishino Y, Narumi I (2015) DNA repair in hyperthermophilic and hyperradioresistant microorganisms. Curr Opin Microbiol 25: 103–112. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2015.05.010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Slade D, Radman M (2011) Oxidative stress resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 75: 133–191. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00015-10 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

