Carvacrol derivatives as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors; synthesis, kinetics mechanism and molecular docking studies
- PMID: 28542395
- PMCID: PMC5441849
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178069
Carvacrol derivatives as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors; synthesis, kinetics mechanism and molecular docking studies
Abstract
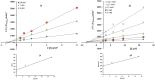
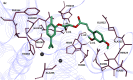
The present work describesthe development of highly potent mushroom tyrosinase inhibitor better than the standard kojic acid. Carvacrol derivatives 4a-f and 6a-d having substituted benzoic acid and cinnamic acidresidues were synthesized with the aim to possess potent tyrosinase inhibitory activity.The structures of the synthesized compounds were ascertained by their spectroscopic data (FTIR, 1HNMR, 13CNMR and Mass Spectroscopy).Mushroom tyrosinase inhibitory activity of synthesized compounds was determined and it was found that one of the derivative 6c possess higher activity (IC50 0.0167μM) than standard kojic acid (IC50 16.69μM). The derivatives 4c and 6b also showed good tyrosinase inhibitory activity with (IC50 16.69μM) and (IC50 16.69μM) respectively.Lineweaver-Burk and Dixon plots were used for the determination of kinetic mechanism of the compounds 4c and 6b and 6c. The kinetic analysis revealed that compounds 4c and 6b showed mixed-type inhibition while 6c is a non-competitive inhibitor having Ki values19 μM, 10 μM, and 0.05 μMrespectively. The enzyme inhibitory kinetics further showed thatcompounds 6b and 6c formed irreversible enzyme inhibitor complex while 4c bind reversibly with mushroom tyrosinase.The docking studies showed that compound 6c have maximum binding affinity against mushroom tyrosinase (PDBID: 2Y9X) with binding energy value (-7.90 kcal/mol) as compared to others.The 2-hydroxy group in compound 6c interacts with amino acid HIS85 which is present in active binding site. The wet lab results are in good agreement with the dry lab findings.Based upon our investigation we may propose that the compound 6c is promising candidate for the development of safe cosmetic agent.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Kinetic and in silico studies of novel hydroxy-based thymol analogues as inhibitors of mushroom tyrosinase.Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Jun 15;98:203-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.05.031. Epub 2015 May 21. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26025140
-
Synthesis, computational studies and enzyme inhibitory kinetics of substituted methyl[2-(4-dimethylamino-benzylidene)-hydrazono)-4-oxo-thiazolidin-5-ylidene]acetates as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 Nov 1;25(21):5929-5938. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.09.009. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28988751
-
Design, synthesis, kinetic mechanism and molecular docking studies of novel 1-pentanoyl-3-arylthioureas as inhibitors of mushroom tyrosinase and free radical scavengers.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Dec 1;141:273-281. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.09.059. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 29040952
-
Structure and inhibition mechanism of some synthetic compounds and phenolic derivatives as tyrosinase inhibitors: review and new insight.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023 Jul;41(10):4798-4810. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2022.2069157. Epub 2022 May 5. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023. PMID: 35510568 Review.
-
Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of paeonol thiosemicarbazone analogues as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors.Int J Biol Macromol. 2013 Nov;62:589-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.09.056. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013. PMID: 24120880 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and tyrosinase inhibitory activities of 4-oxobutanoate derivatives of carvacrol and thymol.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019 Jan 1;29(1):56-58. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.11.013. Epub 2018 Nov 8. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019. PMID: 30446314 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of (Z)-2-benzylidene-dihydroimidazothiazolone derivatives as tyrosinase inhibitors: Anti-melanogenic effects and in silico studies.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Feb 12;20:899-912. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.02.007. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35242283 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-1-(Furan-2-yl)-(substituted phenyl)prop-2-en-1-one Derivatives as Tyrosinase Inhibitors and Melanogenesis Inhibition: An In Vitro and In Silico Study.Molecules. 2020 Nov 21;25(22):5460. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225460. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33233397 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical characterization and multifaceted bioactivity assessment of essential oil from Ptychotis verticillata Duby: Anti-diabetic, anti-tyrosinase, and anti-inflammatory activity.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 9;10(8):e29459. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29459. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38699706 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of immobilized tyrosinase - an enzyme that is stable in organic solvent at 100 °C.RSC Adv. 2018 Nov 27;8(69):39529-39535. doi: 10.1039/c8ra07559j. eCollection 2018 Nov 23. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35558031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Solomon EI, Sundaram UM, Machonkin TE(1996)Multicopper oxidases and oxygenases.Chem. Rev. 96, 2563–2606. - PubMed
-
- Sánchez-Ferrer A, Rodríguez-López JN, García-Cánovas F, García-Carmona F(1995)Tyrosinase: a comprehensive review of its mechanism.Biochem.Biophys.Acta.1247, 1–11. - PubMed
-
- Solminski A,Constantino R (1991a)L-tyrosine induces tyrosinase expression via a posttranscriptional mechanism. Experientia.47, 721–724. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

