Biodegradation of di-n-butyl phthalate by bacterial consortium LV-1 enriched from river sludge
- PMID: 28542471
- PMCID: PMC5444784
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178213
Biodegradation of di-n-butyl phthalate by bacterial consortium LV-1 enriched from river sludge
Abstract
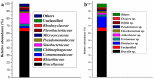
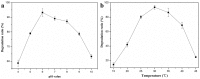
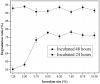
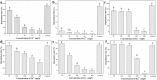
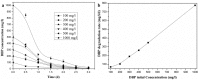
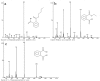
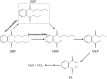
A stable bacterial consortium (LV-1) capable of degrading di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) was enriched from river sludge. Community analysis revealed that the main families of LV-1 are Brucellaceae (62.78%) and Sinobacteraceae (14.83%), and the main genera of LV-1 are Brucella spp. (62.78%) and Sinobacter spp. (14.83%). The optimal pH and temperature for LV-1 to degrade DBP were pH 6.0 and 30°C, respectively. Inoculum size influenced the degradation ratio when the incubation time was < 24 h. The initial concentration of DBP also influenced the degradation rates of DBP by LV-1, and the degradation rates ranged from 69.0-775.0 mg/l/d in the first 24 h. Degradation of DBP was best fitted by first-order kinetics when the initial concentration was < 300 mg/l. In addition, Cd2+, Cr6+, and Zn2+ inhibited DBP degradation by LV-1 at all considered concentrations, but low concentrations of Pb2+, Cu2+, and Mn2+ enhanced DBP degradation. The main intermediates (mono-ethyl phthalate [MEP], mono-butyl phthalate [MBP], and phthalic acid [PA]) were identified in the DBP degradation process, thus a new biochemical pathway of DBP degradation is proposed. Furthermore, LV-1 also degraded other phthalates with shorter ester chains (DMP, DEP, and PA).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Wu XL, Wang YY, Liang RX, Dai QY, Chao WL. Degradation of di-n-butyl phthalate by newly isolated Ochrobactrum sp. B Environ Contam Tox. 2010a; 85: 235–237. - PubMed
-
- Fang CR, Yao J, Zheng YG, Jiang CJ, Hu LF, Wu YY, et al. Dibutyl phthalate degradation by Enterobacter sp. T5 isolated from municipal solid waste in landfill bioreactor. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad. 2010; 64: 442–446.
-
- Wang YY, Miao B, Hou DM, Wu XL, Peng B. Biodegradation of di-n-butyl phthalate and expression of the 3, 4-phthalate dioxygenase gene in Arthrobacter sp. ZH2 strain. Process Biochem. 2012; 47: 936–940.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

