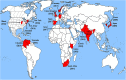
Candida auris: A rapidly emerging cause of hospital-acquired multidrug-resistant fungal infections globally
- PMID: 28542486
- PMCID: PMC5436850
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006290
Candida auris: A rapidly emerging cause of hospital-acquired multidrug-resistant fungal infections globally
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures
References
-
- Vincent JL, Rello J, Marshall J, Silva E, Anzueto A, Martin CD, et al. International study of the prevalence and outcomes of infection in intensive care units. JAMA 2009;302:2323–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1754 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim MN, Shin JH, Sung H, Lee K, Kim EC, Ryoo N, et al. Candida haemulonii and closely related species at 5 university hospitals in Korea: identification, antifungal susceptibility, and clinical features. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:e57–61. doi: 10.1086/597108 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lee WG, Shin JH, Uh Y, Kang MG, Kim SH, Park KH, et al. First three reported cases of nosocomial fungemia caused by Candida auris. J Clin Microbiol 2011;49:3139–42. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00319-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chowdhary A, Sharma C, Duggal S, Agarwal K, Prakash A, Singh PK, et al. New clonal strain of Candida auris, Delhi, India. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:1670–73. doi: 10.3201/eid1910.130393 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chowdhary A, Anil Kumar V, Sharma C, Prakash A, Agarwal K, Babu R, et al. Multidrug-resistant endemic clonal strain of Candida auris in India. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;33:919–26. doi: 10.1007/s10096-013-2027-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical