Relating quantitative variation within a behavior to variation in transcription
- PMID: 28542920
- PMCID: PMC5555821
- DOI: 10.1111/evo.13273
Relating quantitative variation within a behavior to variation in transcription
Abstract
Many studies have shown that variation in transcription is associated with changes in behavioral state, or with variation within a state, but little has been done to address if the same genes are involved in both. Here, we investigate the transcriptional basis of variation in parental provisioning using two species of burying beetle, Nicrophorus orbicollis and Nicrophorus vespilloides. We used RNA-seq to compare transcription in parents that provided high amounts of provisioning behavior versus low amounts in males and females of each species. We found no overarching transcriptional patterns distinguishing high from low caring parents, and no informative transcripts that displayed particularly large expression differences in either sex. However, we did find subtler gene expression differences between high and low provisioning parents that are consistent across both sexes and species. Furthermore, we show that transcripts previously implicated in transitioning into parental care in N. vespilloides had high variance in the levels of transcription and were unusually likely to display differential expression between high and low provisioning parents. Thus, quantitative behavioral variation appears to reflect many transcriptional differences of small effect. Furthermore, the same transcripts required for the transition between behavioral states are also related to variation within a behavioral state.
Keywords: Nicrophorus; RNA-seq; burying beetle; gene set enrichment analysis; parental care; quantitative trait transcripts.
© 2017 The Author(s). Evolution © 2017 The Society for the Study of Evolution.
Figures
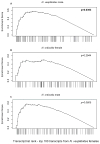
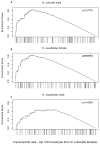
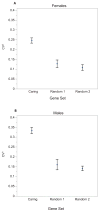
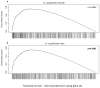
Comment in
-
Digest: Using transcriptomics to map parental care behavior in burying beetles.Evolution. 2017 Aug;71(8):2132-2133. doi: 10.1111/evo.13301. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Evolution. 2017. PMID: 28685894 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Difference in parenting in two species of burying beetle, Nicrophorus orbicollis and Nicrophorus vespilloides.J Ethol. 2016 Sep;34(3):315-319. doi: 10.1007/s10164-016-0477-5. Epub 2016 Jun 28. J Ethol. 2016. PMID: 27917015 Free PMC article.
-
From facultative to obligatory parental care: Interspecific variation in offspring dependency on post-hatching care in burying beetles.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 5;6:29323. doi: 10.1038/srep29323. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27378180 Free PMC article.
-
Biparental care is predominant and beneficial to parents in the burying beetle Nicrophorus orbicollis (Coleoptera: Silphidae).Biol J Linn Soc Lond. 2016 Dec;119(4):1082-1088. doi: 10.1111/bij.12830. Epub 2016 May 26. Biol J Linn Soc Lond. 2016. PMID: 28025585 Free PMC article.
-
A gene associated with social immunity in the burying beetle Nicrophorus vespilloides.Proc Biol Sci. 2016 Jan 27;283(1823):20152733. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2015.2733. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Proc Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26817769 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomes of parents identify parenting strategies and sexual conflict in a subsocial beetle.Nat Commun. 2015 Sep 29;6:8449. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9449. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26416581 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Changes of gene expression but not cytosine methylation are associated with male parental care reflecting behavioural state, social context and individual flexibility.J Exp Biol. 2019 Jan 16;222(Pt 2):jeb188649. doi: 10.1242/jeb.188649. J Exp Biol. 2019. PMID: 30446546 Free PMC article.
-
Offspring reverse transcriptome responses to maternal deprivation when reared with pathogens in an insect with facultative family life.Proc Biol Sci. 2020 May 13;287(1926):20200440. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2020.0440. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Proc Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32345162 Free PMC article.
-
takeout gene expression is associated with temporal kin recognition.R Soc Open Sci. 2023 Aug 23;10(8):230860. doi: 10.1098/rsos.230860. eCollection 2023 Aug. R Soc Open Sci. 2023. PMID: 37621661 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of food source availability in the salivary gland transcriptome of the unique burying beetle Nicrophorus pustulatus (Coleoptera: Silphidae).PLoS One. 2021 Sep 23;16(9):e0255660. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255660. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34555059 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenomic landscape associated with status-dependent cooperative behaviour.Mol Ecol. 2025 Aug;34(15):e17327. doi: 10.1111/mec.17327. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Mol Ecol. 2025. PMID: 38511765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert FW, Kruglyak L. The role of regulatory variation in complex traits and disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2015;16:197–212. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
