Substance use disorders in prisoners: an updated systematic review and meta-regression analysis in recently incarcerated men and women
- PMID: 28543749
- PMCID: PMC5589068
- DOI: 10.1111/add.13877
Substance use disorders in prisoners: an updated systematic review and meta-regression analysis in recently incarcerated men and women
Abstract
Aims: The aims were to (1) estimate the prevalence of alcohol and drug use disorders in prisoners on reception to prison and (2) estimate and test sources of between study heterogeneity.
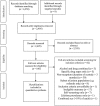
Methods: Studies reporting the 12-month prevalence of alcohol and drug use disorders in prisoners on reception to prison from 1 January 1966 to 11 August 2015 were identified from seven bibliographic indexes. Primary studies involving clinical interviews or validated instruments leading to DSM or ICD diagnoses were included; self-report surveys and investigations that assessed individuals more than 3 months after arrival to prison were not. Random-effects meta-analysis and subgroup and meta-regression analyses were conducted. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were followed.
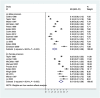
Results: In total, 24 studies with a total of 18 388 prisoners across 10 countries were identified. The random-effects pooled prevalence estimate of alcohol use disorder was 24% [95% confidence interval (CI) = 21-27], with very high heterogeneity (I2 = 94%). These ranged from 16 to 51% in male and 10-30% in female prisoners. For drug use disorders, there was evidence of heterogeneity by sex, and the pooled prevalence estimate in male prisoners was 30% (95% CI = 22-38; I2 = 98%; 13 studies; range 10-61%) and, in female prisoners, was 51% (95% CI = 43-58; I2 = 95%; 10 studies; range 30-69%). On meta-regression, sources of heterogeneity included higher prevalence of drug use disorders in women, increasing rates of drug use disorders in recent decades, and participation rate.
Conclusions: Substance use disorders are highly prevalent in prisoners. Approximately a quarter of newly incarcerated prisoners of both sexes had an alcohol use disorder, and the prevalence of a drug use disorder was at least as high in men, and higher in women.
© 2017 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures

Comment in
-
Commentary on Fazel et al. (2017): High levels of substance use disorders among correctional inmates-some implications for interventions of the review data from Fazel et al.Addiction. 2017 Oct;112(10):1740-1741. doi: 10.1111/add.13969. Addiction. 2017. PMID: 28891149 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pratt D., Appleby L., Piper N., Webb R., Shaw J. Suicide in recently released prisoners: a case–control study. Psychol Med 2010; 40: 827–835. - PubMed
-
- Kinner S. A., Forsyth S., Williams G. Systematic review of record linkage studies of mortality in ex‐prisoners: why (good) methods matter. Addiction 2013; 108: 38–49. - PubMed
-
- Baillargeon J., Binswanger I. A., Penn J. V., Williams B. A., Murray O. J. Psychiatric disorders and repeat incarcerations: the revolving prison door. Am J Psychiatry 2009; 166: 103–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

