Application of molecular, microbiological, and immunological tests for the diagnosis of bone and joint tuberculosis
- PMID: 28543876
- PMCID: PMC6816924
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22260
Application of molecular, microbiological, and immunological tests for the diagnosis of bone and joint tuberculosis
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the application of interferon gamma release assay (IGRA), rifampicin resistant real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR technique Xpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis/rifampicin (Xpert MTB/RIF), and the levels of TNF-α and TGF-β in the diagnosis of bone and joint tuberculosis.
Methods: Eighty-six patients with bone and joint tuberculosis, diagnosed by pathology or microbiology, were examined by Xpert MTB/RIF and IGRA (T-SPOT. TB) for Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, and the TNF-α and TGF-β levels of the patients were measured.
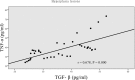
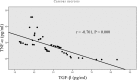
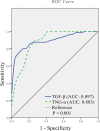
Results: The sensitivity of IGRA in diagnosing bone and joint tuberculosis was 81.4%; Xpert MTB/RIF's sensitivity was 70.9%. The combined sensitivity of the two methods was 91.9%. The combined detection sensitivity of the two methods was higher than individual IGRA or Xpert MTB/RIF detection sensitivity. The TNF-α and TGF-β levels in bone and joint tuberculosis patients were higher than those in the control group.
Conclusion: Xpert MTB/RIF, IGRA, TNF-α, and TGF-βs expression have value in the rapid diagnosis of bone and joint tuberculosis, and the sensitivity and accuracy of bone and joint tuberculosis diagnosis by combining them can improve it.
Keywords: TGF-β; TNF-α; Xpert; bone and joint tuberculosis; γ-interferon.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Misra SP, Misra V, Dwivedi M, Gupta SC. Colonic tuberculosis: clinical features, endoscopic appearance and management. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999;14:723‐729. - PubMed
-
- Lesic A, Bumbasirevic M, Savic B, Cobeljic G, Pesut D. Current diagnosis and treatment of the osteoarticular tuberculosis. Srp Arh Celok Lek 2004;132:345‐351. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources