"Heat shock protein 70 in pancreatic diseases: Friend or foe"
- PMID: 28543919
- PMCID: PMC5714583
- DOI: 10.1002/jso.24653
"Heat shock protein 70 in pancreatic diseases: Friend or foe"
Abstract
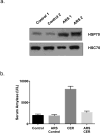
The heat shock response in pancreatitis that is activated via HSP70 protects acinar cells through multiple simultaneous mechanisms. It inhibits trypsinogen activation and modulates NF-κB signaling to limit acinar cell injury. On the other hand, HSP70 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and is hijacked by the cellular machinery to inhibit apoptosis. Inhibition of HSP70 in pancreatic cancer by a novel compound, Minnelide, has shown considerable clinical promise.
Keywords: HSP70; calcium; lysosomes; minnelide; pancreatic cancer; pancreatitis; triptolide.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Kregel KC. Invited Review: Heat shock proteins: modifying factors in physiological stress responses and acquired thermotolerance. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2002;92:2177–2186. - PubMed
-
- Li GC, Meyer JL, Mak JY, Hahn GM. Heat-induced protection of mice against thermal death. Cancer Res. 1983;43:5758–5760. - PubMed
-
- Landry J, Bernier D, Chretien P, et al. Synthesis and degradation of heat shock proteins during development and decay of thermotolerance. Cancer Res. 1982;42:2457–2461. - PubMed
-
- Landry J, Chretien P. Relationship between hyperthermia-induced heat-shock proteins and thermotolerance in Morris hepatoma cells. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983;61:428–437. - PubMed
-
- Guttman SD, Glover CV, Allis CD, Gorovsky MA. Heat shock, deciliation and release from anoxia induce the synthesis of the same set of polypeptides in starved T. pyriformis. Cell. 1980;22:299–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

