Genome-wide mediation analysis of psychiatric and cognitive traits through imaging phenotypes
- PMID: 28544218
- PMCID: PMC5568842
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.23650
Genome-wide mediation analysis of psychiatric and cognitive traits through imaging phenotypes
Abstract
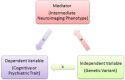
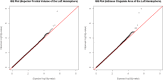
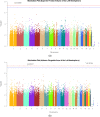
Heritability is well documented for psychiatric disorders and cognitive abilities which are, however, complex, involving both genetic and environmental factors. Hence, it remains challenging to discover which and how genetic variations contribute to such complex traits. In this article, they propose to use mediation analysis to bridge this gap, where neuroimaging phenotypes were utilized as intermediate variables. The Philadelphia Neurodevelopmental Cohort was investigated using genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and mediation analyses. Specifically, 951 participants were included with age ranging from 8 to 21 years. Two hundred and four neuroimaging measures were extracted from structural magnetic resonance imaging scans. GWAS were conducted for each measure to evaluate the SNP-based heritability. Furthermore, mediation analyses were employed to understand the mechanisms in which genetic variants have influence on pathological behaviors implicitly through neuroimaging phenotypes, and identified SNPs that would not be detected otherwise. Our analyses found that rs10494561, located in the intron region within NMNAT2, was associated with the severity of the prodromal symptoms of psychosis implicitly, mediated through the volume of the left hemisphere of the superior frontal region ( P=2.38×10-8). The gene NMNAT2 is known to be associated with brainstem degeneration, and produce cytoplasmic enzyme which is mainly expressed in the brain. Another SNP rs2285351 was found in the intron region of gene IFT122 which may be potentially associated with human spatial orientation ability through the area of the left hemisphere of the isthmuscingulate region ( P=3.70×10-8). Hum Brain Mapp 38:4088-4097, 2017. © 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: genome-wide association studies; imaging genetics; intermediate phenotypes; neuroimaging measures.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Heritable Cognitive Ability and Psychopathology With White Matter Properties in Children and Adolescents.JAMA Psychiatry. 2018 Mar 1;75(3):287-295. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.4277. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29365026 Free PMC article.
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Heritability of Behavior Problems in Childhood: Genome-Wide Complex Trait Analysis.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2015 Sep;54(9):737-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 20. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26299295
-
Early developmental gene enhancers affect subcortical volumes in the adult human brain.Hum Brain Mapp. 2016 May;37(5):1788-800. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23136. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016. PMID: 26890892 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond heritability: improving discoverability in imaging genetics.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 May 1;27(R1):R22-R28. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy082. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29522091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New technologies provide insights into genetic basis of psychiatric disorders and explain their co-morbidity.Psychiatr Danub. 2010 Jun;22(2):190-2. Psychiatr Danub. 2010. PMID: 20562745 Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging Genetic Based Mediation Analysis for Human Cognition.Front Neurosci. 2022 Apr 28;16:824069. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.824069. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35573299 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide brain DNA methylation analysis suggests epigenetic reprogramming in Parkinson disease.Neurol Genet. 2019 Jun 24;5(4):e342. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000342. eCollection 2019 Aug. Neurol Genet. 2019. PMID: 31403079 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Imaging Genomics: Integrated Analysis and Machine Learning.Proc IEEE Inst Electr Electron Eng. 2020 Jan;108(1):125-162. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2947272. Epub 2019 Oct 29. Proc IEEE Inst Electr Electron Eng. 2020. PMID: 31902950 Free PMC article.
-
Mediation model with a categorical exposure and a censored mediator with application to a genetic study.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 12;16(10):e0257628. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257628. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34637449 Free PMC article.
-
Mediation Analysis for High-Dimensional Mediators and Outcomes with an Application to Multimodal Imaging Data.Comput Stat Data Anal. 2023 Sep;185:107765. doi: 10.1016/j.csda.2023.107765. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Comput Stat Data Anal. 2023. PMID: 37251499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baron RM, Kenny DA (1986): The moderator‐mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol 51:1173–1182. - PubMed
-
- Belmonte MK, Cook E, Anderson GM, Rubenstein JL, Greenough WT, Beckel‐Mitchener A, Courchesne E, Boulanger LM, Powell SB, Levitt PR, Perry EK, Jiang YH, DeLorey TM, Tierney E (2004): Autism as a disorder of neural information processing: Directions for research and targets for therapy. Mol Psychiatry 9:646–663. - PubMed
-
- Bertram L, McQueen MB, Mullin K, Blacker D, Tanzi RE (2007): Systematic meta‐analyses of Alzheimer disease genetic association studies: The alzgene database. Nat Genet 39:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Davies G, Tenesa A, Payton A, Yang J, Harris SE, Liewald D, Ke X, Le Hellard S, Christoforou A, Luciano M, McGhee K, Lopez L, Gow AJ, Corley J, Redmond P, Fox HC, Haggarty P, Whalley LJ, McNeill G, Goddard ME, Espeseth T, Lundervold AJ, Reinvang I, Pickles A, Steen VM, Ollier W, Porteous DJ, Horan M, Starr JM, Pendleton N, Visscher PM, Deary IJ (2011): Genome‐wide association studies establish that human intelligence is highly heritable and polygenic. Mol Psychiatry 16:996–1005. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

