Podocyte Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasomes Contributes to the Development of Proteinuria in Lupus Nephritis
- PMID: 28544564
- PMCID: PMC5568813
- DOI: 10.1002/art.40155
Podocyte Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasomes Contributes to the Development of Proteinuria in Lupus Nephritis
Abstract
Objective: Development of proteinuria in lupus nephritis (LN) is associated with podocyte dysfunction. The NLRP3 inflammasome has been implicated in the pathogenesis of LN. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether NLRP3 inflammasome activation is involved in the development of podocyte injury in LN.
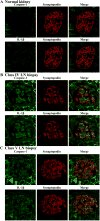
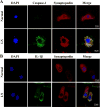
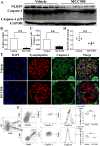
Methods: A fluorescence-labeled caspase 1 inhibitor probe was used to detect the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes in podocytes derived from lupus-prone NZM2328 mice and from renal biopsy tissues obtained from patients with LN. MCC950, a selective inhibitor of NLRP3, was used to treat NZM2328 mice. Proteinuria, podocyte ultrastructure, and renal pathology were evaluated. In vitro, sera from diseased NZM2328 mice were used to stimulate a podocyte cell line, and the cells were analyzed by flow cytometry.
Results: NLRP3 inflammasomes were activated in podocytes from lupus-prone mice and from patients with LN. Inhibition of NLRP3 with MCC950 ameliorated proteinuria, renal histologic lesions, and podocyte foot process effacement in lupus-prone mice. In vitro, sera from diseased NZM2328 mice activated NLRP3 inflammasomes in the podocyte cell line through the production of reactive oxygen species.
Conclusion: NLRP3 inflammasomes were activated in podocytes from lupus-prone mice and from LN patients. Activation of NLRP3 is involved in the pathogenesis of podocyte injuries and the development of proteinuria in LN.
© 2017, American College of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
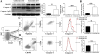
Comment in
-
Editorial: Podocytes as Active Participants in Lupus Nephritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Aug;69(8):1517-1520. doi: 10.1002/art.40157. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28544537 No abstract available.
-
Lupus nephritis: NLRP3 inflammasome ignites podocyte dysfunction.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017 Aug;13(8):451. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2017.97. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28592896 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome ameliorates podocyte damage by suppressing lipid accumulation in diabetic nephropathy.Metabolism. 2021 May;118:154748. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154748. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Metabolism. 2021. PMID: 33675822
-
Pathogenesis of lupus nephritis: RIP3 dependent necroptosis and NLRP3 inflammasome activation.J Autoimmun. 2019 Sep;103:102286. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.05.014. Epub 2019 May 24. J Autoimmun. 2019. PMID: 31133359 Free PMC article.
-
Novel approach to alleviate lupus nephritis: targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in CD8+CD69+CD103+ TRM cells.J Transl Med. 2024 Dec 23;22(1):1139. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05951-9. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39716284 Free PMC article.
-
Target of MCC950 in Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: a Literature Review.Inflammation. 2020 Feb;43(1):17-23. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01098-8. Inflammation. 2020. PMID: 31646445 Review.
-
MCC950 in the treatment of NLRP3-mediated inflammatory diseases: Latest evidence and therapeutic outcomes.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 May;106:108595. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108595. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35124417 Review.
Cited by
-
Ferroptosis in lymphoma: Emerging mechanisms and a novel therapeutic approach.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 3;13:1039951. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1039951. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36406116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NLRP3 inflammasome activation from Kupffer cells is involved in liver fibrosis of Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice via NF-κB.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Jan 11;12(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-3223-8. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 30635040 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine for lupus nephritis: modulation of autoimmune pathogenesis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 2;16:1523272. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1523272. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40385489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Podocyte A20/TNFAIP3 Controls Glomerulonephritis Severity via the Regulation of Inflammatory Responses and Effects on the Cytoskeleton.Cells. 2025 Mar 5;14(5):381. doi: 10.3390/cells14050381. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40072109 Free PMC article.
-
Therapy Targeted to the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Chronic Kidney Disease.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2024 May 30;10(5):369-383. doi: 10.1159/000539496. eCollection 2024 Oct. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39430292 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gregersen JW, Jayne DR. B-cell depletion in the treatment of lupus nephritis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8:505–14. - PubMed
-
- Faurschou M, Dreyer L, Kamper AL, Starklint H, Jacobsen S. Long-term mortality and renal outcome in a cohort of 100 patients with lupus nephritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2010;62:873–80. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Yu F, Song D, Wang SX, Zhao MH. Podocyte involvement in lupus nephritis based on the 2003 ISN/RPS system: a large cohort study from a single centre. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2014;53:1235–44. - PubMed
-
- Cellesi F, Li M, Rastaldi MP. Podocyte injury and repair mechanisms. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2015;24:239–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

