Efficacy of Mycophenolate Mofetil and Oral Cyclophosphamide on Skin Thickness: Post Hoc Analyses From Two Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials
- PMID: 28544580
- PMCID: PMC5700860
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.23282
Efficacy of Mycophenolate Mofetil and Oral Cyclophosphamide on Skin Thickness: Post Hoc Analyses From Two Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials
Abstract
Objective: To assess the efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and cyclophosphamide (CYC) on modified Rodnan skin score (MRSS) in participants enrolled in the Scleroderma Lung Study (SLS) I and II.
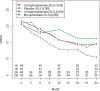
Methods: SLS I participants received daily oral CYC or matching placebo for 1 year, whereas SLS II participants received daily MMF for 2 years or daily oral CYC for 1 year followed by placebo for second year. We assessed the impact of MMF and CYC on the MRSS in SLS II over a 24-month period. We also compared the change in MRSS in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc) assigned to CYC and MMF in SLS II and SLS I versus placebo in SLS I over a 24-month period using a linear mixed model.
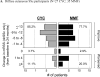
Results: In SLS II, the baseline mean ± SD MRSS was 14.0 ± 10.6 units for CYC and 15.3 ± 10.4 units for MMF; 58.5% were classified as dcSSc. CYC and MMF were associated with statistically significant improvements in MRSS from baseline over the period of 24 months in dcSSc (P < 0.05 at each time point), but there were no differences between the 2 groups. In the dcSSc subgroup, the change in MRSS from baseline to all 6-month visits was similar in SLS II groups (MMF, CYC, pooled cohort [MMF + CYC]) and in the SLS I CYC group and showed statistically significant improvements compared to SLS I placebo at 12, 18, and 24 months (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: In SLS II, MMF and CYC treatment resulted in improvements in MRSS in patients with dcSSc over 24 months. In addition, MMF and CYC treatment resulted in statistically significant improvements in MRSS in patients with dcSSc when compared with the SLS I placebo group.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00004563 NCT00883129.
© 2017, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

References
-
- Amjadi S, Maranian P, Furst DE, Clements PJ, Wong WK, Postlethwaite AE, et al. Course of the modified Rodnan skin thickness score in systemic sclerosis clinical trials: analysis of three large multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled trials. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2009;60(8):2490–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clements P, Lachenbruch P, Siebold J, White B, Weiner S, Martin R, et al. Inter and intraobserver variability of total skin thickness score (modified Rodnan TSS) in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 1995;22(7):1281–5. - PubMed
-
- Khanna D, Denton CP, Jahreis A, van Laar JM, Frech TM, Anderson ME, et al. Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous tocilizumab in adults with systemic sclerosis (faSScinate): a phase 2, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. 2016 - PubMed
-
- Pope JE, Bellamy N, Seibold JR, Baron M, Ellman M, Carette S, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of methotrexate versus placebo in early diffuse scleroderma. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2001;44(6):1351–8. - PubMed
-
- van den Hoogen FH, Boerbooms AM, Swaak AJ, Rasker JJ, van Lier HJ, van de Putte LB. Comparison of methotrexate with placebo in the treatment of systemic sclerosis: a 24 week randomized double-blind trial, followed by a 24 week observational trial. British journal of rheumatology. 1996;35(4):364–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

