Estrogen receptor β deficiency impairs BDNF-5-HT2A signaling in the hippocampus of female brain: A possible mechanism for menopausal depression
- PMID: 28544903
- PMCID: PMC5523821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2017.05.016
Estrogen receptor β deficiency impairs BDNF-5-HT2A signaling in the hippocampus of female brain: A possible mechanism for menopausal depression
Abstract
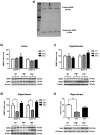
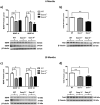
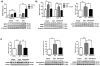
Depression currently affects 350 million people worldwide and 19 million Americans each year. Women are 2.5 times more likely to experience major depression than men, with some women appearing to be at a heightened risk during the menopausal transition. Estrogen signaling has been implicated in the pathophysiology of mood disorders including depression; however, the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. In this study, the role of estrogen receptor (ER) subtypes, ERα and ERβ, in the regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and serotonin (5-HT) signaling was investigated; two pathways that have been hypothesized to be interrelated in the etiology of depression. The analyses in ERα-/- and ERβ-/- mouse models demonstrated that BDNF was significantly downregulated in ERβ-/- but not ERα-/- mice, and the ERβ-/--mediated effect was brain-region specific. A 40% reduction in BDNF protein expression was found in the hippocampus of ERβ-/- mice; in contrast, the changes in BDNF were at a much smaller magnitude and insignificant in the cortex and hypothalamus. Further analyses in primary hippocampal neurons indicated that ERβ agonism significantly enhanced BDNF/TrkB signaling and the downtream cascades involved in synaptic plasticity. Subsequent study in ERβ mutant rat models demonstrated that disruption of ERβ was associated with a significantly elevated level of 5-HT2A but not 5-HT1A in rat hippocampus, indicating ERβ negatively regulates 5-HT2A. Additional analyses in primary neuronal cultures revealed a significant association between BDNF and 5-HT2A pathways, and the data showed that TrkB activation downregulated 5-HT2A whereas activation of 5-HT2A had no effect on BDNF, suggesting that BDNF/TrkB is an upstream regulator of the 5-HT2A pathway. Collectively, these findings implicate that the disruption in estrogen homeostasis during menopause leads to dysregulation of BDNF-5-HT2A signaling and weakened synaptic plasticity, which together predispose the brain to a vulnerable state for depression. Timely intervention with an ERβ-targeted modulator could potentially attenuate this susceptibility and reduce the risk or ameliorate the clinical manifestation of this brain disorder.
Keywords: 5-HT(1A); 5-HT(2A); Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); Estrogen receptor β (ERβ); Hippocampus; Menopausal depression.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Calabrese F, Guidotti G, Racagni G, Riva MA. Reduced neuroplasticity in aged rats: a role for the neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neurobiology of aging. 2013;34:2768–2776. - PubMed
-
- Cameron S, Wallis C, Blakely A. Setting up an HIV-testing service with same-day results. Nursing times. 1995;91:33–34. - PubMed
-
- Campbell KE, Dennerstein L, Finch S, Szoeke CE. Impact of menopausal status on negative mood and depressive symptoms in a longitudinal sample spanning 20 years. Menopause. 2017;24:490–496. - PubMed
-
- Cavus I, Duman RS. Influence of estradiol, stress, and 5-HT2A agonist treatment on brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in female rats. Biological psychiatry. 2003;54:59–69. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

