Rapid diagnostic tests for typhoid and paratyphoid (enteric) fever
- PMID: 28545155
- PMCID: PMC5458098
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008892.pub2
Rapid diagnostic tests for typhoid and paratyphoid (enteric) fever
Abstract
Background: Differentiating both typhoid (Salmonella Typhi) and paratyphoid (Salmonella Paratyphi A) infection from other causes of fever in endemic areas is a diagnostic challenge. Although commercial point-of-care rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) for enteric fever are available as alternatives to the current reference standard test of blood or bone marrow culture, or to the widely used Widal Test, their diagnostic accuracy is unclear. If accurate, they could potentially replace blood culture as the World Health Organization (WHO)-recommended main diagnostic test for enteric fever.
Objectives: To assess the diagnostic accuracy of commercially available rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) and prototypes for detecting Salmonella Typhi or Paratyphi A infection in symptomatic persons living in endemic areas.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group Specialized Register, MEDLINE, Embase, Science Citation Index, IndMED, African Index Medicus, LILACS, ClinicalTrials.gov, and the World Health Organization (WHO) International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) up to 4 March 2016. We manually searched WHO reports, and papers from international conferences on Salmonella infections. We also contacted test manufacturers to identify studies.
Selection criteria: We included diagnostic accuracy studies of enteric fever RDTs in patients with fever or with symptoms suggestive of enteric fever living in endemic areas. We classified the reference standard used as either Grade 1 (result from a blood culture and a bone marrow culture) or Grade 2 (result from blood culture and blood polymerase chain reaction, or from blood culture alone).
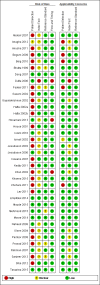
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted the test result data. We used a modified QUADAS-2 extraction form to assess methodological quality. We performed a meta-analysis when there were sufficient studies for the test and heterogeneity was reasonable.
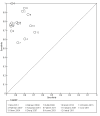
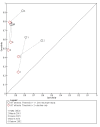
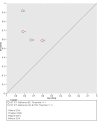
Main results: Thirty-seven studies met the inclusion criteria and included a total of 5080 participants (range 50 to 1732). Enteric fever prevalence rates in the study populations ranged from 1% to 75% (median prevalence 24%, interquartile range (IQR) 11% to 46%). The included studies evaluated 16 different RDTs, and 16 studies compared two or more different RDTs. Only three studies used the Grade 1 reference standard, and only 11 studies recruited unselected febrile patients. Most included studies were from Asia, with five studies from sub-Saharan Africa. All of the RDTs were designed to detect S.Typhi infection only.Most studies evaluated three RDTs and their variants: TUBEX in 14 studies; Typhidot (Typhidot, Typhidot-M, and TyphiRapid-Tr02) in 22 studies; and the Test-It Typhoid immunochromatographic lateral flow assay, and its earlier prototypes (dipstick, latex agglutination) developed by the Royal Tropical Institute, Amsterdam (KIT) in nine studies. Meta-analyses showed an average sensitivity of 78% (95% confidence interval (CI) 71% to 85%) and specificity of 87% (95% CI 82% to 91%) for TUBEX; and an average sensitivity of 69% (95% CI 59% to 78%) and specificity of 90% (95% CI 78% to 93%) for all Test-It Typhoid and prototype tests (KIT). Across all forms of the Typhidot test, the average sensitivity was 84% (95% CI 73% to 91%) and specificity was 79% (95% CI 70% to 87%). When we based the analysis on the 13 studies of the Typhidot test that either reported indeterminate test results or where the test format means there are no indeterminate results, the average sensitivity was 78% (95% CI 65% to 87%) and specificity was 77% (95% CI 66% to 86%). We did not identify any difference in either sensitivity or specificity between TUBEX, Typhidot, and Test-it Typhoid tests when based on comparison to the 13 Typhidot studies where indeterminate results are either reported or not applicable. If TUBEX and Test-it Typhoid are compared to all Typhidot studies, the sensitivity of Typhidot was higher than Test-it Typhoid (15% (95% CI 2% to 28%), but other comparisons did not show a difference at the 95% level of CIs.In a hypothetical cohort of 1000 patients presenting with fever where 30% (300 patients) have enteric fever, on average Typhidot tests reporting indeterminate results or where tests do not produce indeterminate results will miss the diagnosis in 66 patients with enteric fever, TUBEX will miss 66, and Test-It Typhoid and prototype (KIT) tests will miss 93. In the 700 people without enteric fever, the number of people incorrectly diagnosed with enteric fever would be 161 with Typhidot tests, 91 with TUBEX, and 70 with Test-It Typhoid and prototype (KIT) tests. The CIs around these estimates were wide, with no difference in false positive results shown between tests.The quality of the data for each study was evaluated using a standardized checklist called QUADAS-2. Overall, the certainty of the evidence in the studies that evaluated enteric fever RDTs was low.
Authors' conclusions: In 37 studies that evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of RDTs for enteric fever, few studies were at a low risk of bias. The three main RDT tests and variants had moderate diagnostic accuracy. There was no evidence of a difference between the average sensitivity and specificity of the three main RDT tests. More robust evaluations of alternative RDTs for enteric fever are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
LW and CMP are authors of Moore 2014 and Maude 2015. SM has no known conflicts of interest.
Figures













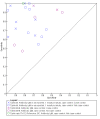

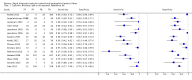
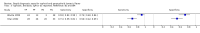
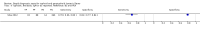



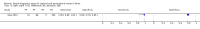
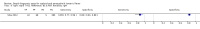
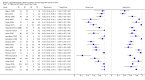
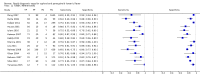

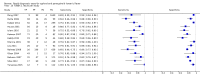

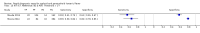
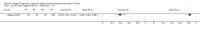

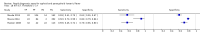




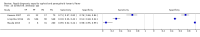

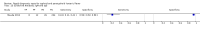
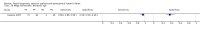
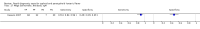


Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Abdoel 2007 {published data only}
-
- Abdoel TH, Pastoor R, Smits HL, Hatta M. Laboratory evaluation of a simple and rapid latex agglutination assay for the serodiagnosis of typhoid fever. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2007;101(10):1032‐8. - PubMed
Anagha 2012 {published data only}
-
- Anagha K, Deepika B, Shahriar R, Sanjeev K. The easy and early diagnosis of typhoid fever. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research 2012;6(2):198‐9.
Anusha 2011 {published data only}
-
- Anusha R, Ganesh R, Lalitha J. Comparison of a rapid commercial test, Enterocheck WB®, with automated blood culture for diagnosis of typhoid fever. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics 2011;31(3):231‐4. - PubMed
Begum 2009 {published data only}
-
- Begum Z, Hossain MA, Musa AK, Shamsuzzaman AK, Mahmud MC, Ahsan MM, et al. Comparison between DOT EIA IgM and Widal Test as early diagnosis of typhoid fever. Mymensingh Medical Journal 2009;18(1):13‐7. - PubMed
Beig 2010 {published data only}
-
- Beig FK, Ahmad F, Ekram M, Shukla I. Typhidot M and Diazo test vis‐à‐vis blood culture and Widal Test in the early diagnosis of typhoid fever in children in a resource poor setting. Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases 2010;14(6):589‐93. - PubMed
Bhutta 1999 {published data only}
-
- Bhutta ZA, Mansurali N. Rapid serologic diagnosis of pediatric typhoid fever in an endemic area: a prospective comparative evaluation of two dot‐enzyme immunoassays and the Widal Test. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1999;61(4):654‐7. - PubMed
Dong 2007 {published data only}
Dutta 2006 {published data only}
-
- Dutta S, Sur D, Manna B, Sen B, Deb AK, Deen JL, et al. Evaluation of new‐generation serologic tests for the diagnosis of typhoid fever: data from a community‐based surveillance in Calcutta, India. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 2006;56(4):359‐65. - PubMed
Fadeel 2011 {published data only}
-
- Fadeel MA, House BL, Wasfy MM, Klena JD, Habashy EE, Said MM, et al. Evaluation of a newly developed ELISA against Widal, TUBEX‐TF and Typhidot for typhoid fever surveillance. Journal of Infection in Developing Countries 2011;5(3):169‐75. - PubMed
Gasem 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gasem MH, Smits HL, Goris MGA, Dolmans WMV. Evaluation of a simple and rapid dipstick assay for the diagnosis of typhoid fever in Indonesia. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2002;51(2):173‐7. - PubMed
Gopalakrishnan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gopalakrishnan V, Sekhar WY, Soo EH, Vinsent RA, Devi S. Typhoid fever in Kuala Lumpur and a comparative evaluation of two commercial diagnostic kits for the detection of antibodies to Salmonella Typhi. Singapore Medical Journal 2002;43(7):354‐8. - PubMed
Hatta 2002a {published data only}
-
- Hatta M, Goris MGA, Heerkens E, Gooskens J, Smits HL. Simple dipstick assay for the detection of Salmonella Typhi‐specific IgM antibodies and the evolution of the immune response in patients with typhoid fever. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2002;66(4):416‐21. - PubMed
Hatta 2002b {published data only}
-
- Hatta M, Mubin H, Abdoel T, Smits HL. Antibody response in typhoid fever in endemic Indonesia and the relevance of serology and culture to diagnosis. South East Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 2002;33(4):742‐51. - PubMed
Hosamani 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hosamani MA, Patil AB, Nadagir SD, Madhusudhan NS, Sambrani P. Diagnosis of enteric fever by Widal and two dot‐enzyme immunoassays: utility and difficulties. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology 2013;7(3):2378‐83.
House 2001 {published data only}
Islam 2016 {published data only}
-
- Islam K, Sayeed MA, Hossen E, Khanam F, Charles RC, Andrews J, et al. Comparison of the performance of the TPTest, Tubex, Typhidot and Widal immunodiagnostic assays and blood cultures in detecting patients with typhoid fever in Bangladesh, including using a Bayesian latent class modeling approach. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 2016;10(4):e0004558. - PMC - PubMed
Ismail 2002 {published data only}
Jesudason 2002 {published data only}
-
- Jesudason M, Esther E, Mathai E. Typhidot test to detect IgG and IgM antibodies in typhoid fever. Indian Journal of Medical Research 2002;116:70‐2. - PubMed
Jesudason 2006 {published data only}
-
- Jesudason MV, Sivakumar S. Prospective evaluation of a rapid diagnostic test Typhidot® for typhoid fever. Indian Journal of Medical Research 2006;123(4):513‐6. - PubMed
Kawano 2007 {published data only}
Keddy 2011 {published data only}
Khan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Khan E, Azam F, Ahmed S, Hassan R. Diagnosis of typhoid fever by Dot Enzyme Immunoassay in an endemic region. Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association 2002;52(9):415‐7. - PubMed
Khanna 2015 {published data only}
Khoharo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Khoharo HK. A comparative study of the typhidot (Dot‐EIA) and Widal tests in blood culture positive cases of typhoid fever. Tropical Doctor 2011;41(3):136‐8. - PubMed
Ley 2011 {published data only}
Limpitikul 2014 {published data only}
Maude 2015 {published data only}
Mehmood 2015 {published data only}
Moore 2014 {published data only}
-
- Moore CE, Pan‐Ngum W, Wijedoru LPM, Sona S, Nga TVT, Duy PT, et al. Evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of a typhoid IgM flow assay for the diagnosis of typhoid fever in Cambodian children using a Bayesian latent class model assuming an imperfect gold standard. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2014;90(1):114‐20. [DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0384] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Naheed 2008 {published data only}
-
- Naheed A, Ram PK, Brooks WA, Mintz ED, Hossain MA, Parsons MM, et al. Clinical value of TUBEX™ and Typhidot® rapid diagnostic tests for typhoid fever in an urban community clinic in Bangladesh. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 2008;61(4):381‐6. - PubMed
Olsen 2004 {published data only}
Pastoor 2008 {published data only}
-
- Pastoor R, Hatta M, Abdoel TH, Smits HL. Simple, rapid, and affordable point‐of‐care test for the serodiagnosis of typhoid fever. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 2008;61(2):129‐34. - PubMed
Prasad 2015 {published data only}
-
- Prasad KJ, Oberoi JK, Goel N, Wattal C. Comparative evaluation of two rapid Salmonella‑IgM tests and blood culture in the diagnosis of enteric fever. Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology 2015;33(2):237‐42. - PubMed
Rahman 2007 {published data only}
-
- Rahman M, Siddique AK, Tam FCH, Sharmin S, Rashid H, Iqbal A, et al. Rapid detection of early typhoid fever in endemic community children by the TUBEX® O9‐antibody test. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious DIsease 2007;58(3):275‐81. - PubMed
Sanjeev 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sanjeev H, Nayak S, Pai Asha KB, Rai R, Karnaker V, Ganesh HR. A systematic evaluation of a rapid DOT‐EIA, blood culture, and Widal Test in the diagnosis of typhoid fever. Nitte University Journal of Health Science 2013;3(1):21‐4.
Siba 2012 {published data only}
Tarupiwa 2015 {published data only}
-
- Tarupiwa A, Tapera S, Mtapuri‐Zinyowera S, Gumbo P, Ruhanya V, Gudza‐Mugabe M, et al. Evaluation of TUBEX‐TF and OnSite Typhoid IgG/IgM Combo rapid tests to detect Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi infection during a typhoid outbreak in Harare, Zimbabwe. BioMed Research Notes 2015;8:50. - PMC - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Alejandria 2012 {published data only}
-
- Alejandria M, Concepcion AO, Li RJ, Gutierrez J. The sensitivity and specificity of serologis tests in the diagnosis of typhoid fever in adults: a meta‐analysis. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2012;16(Suppl 1):e393. [DOI: ]
Bakr 2011 {published data only}
Banchuin 1987 {published data only}
-
- Banchuin N, Appassakij H, Sarasombath S, Manatsathit S, Rungpitarangsi B, Komolpit P, et al. Detection of Salmonella typhi protein antigen in serum and urine: a value for diagnosis of typhoid fever in an endemic area. Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology 1987;5(2):155‐9. - PubMed
Banerjee 1984 {published data only}
-
- Banerjee V, Mukherjee A. Comparative evaluation of microtitre and tube agglutination technique for serodiagnosis of enteric fever. Journal of Communicable Diseases 1984;16(1):82‐3. - PubMed
Boomsma 1988 {published data only}
-
- Boomsma LJ. Clinical aspects of typhoid fever in two rural Nigerian hospitals: a prospective study. Tropical and Geographical Medicine 1988;40(2):97‐102. - PubMed
Cardona‐Castro 2000 {published data only}
Castonguay‐Vanier 2013 {published data only}
-
- Castonguay‐Vanier J, Davong V, Bouthasavong L, Sengdetka D, Simmalavong M, Seupsavith A, et al. Evaluation of a simple blood culture amplification and antigen detection method for diagnosis of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi bacteraemia. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2013;51(1):142‐8. - PMC - PubMed
Chaicumpa 1992 {published data only}
Chart 2007 {published data only}
Chatterjee 1988 {published data only}
-
- Chatterjee PP, Mohan M, Talwar V, Rawat S. Evaluation of co‐agglutination test for diagnosis of typhoid fever in children. Indian Journal of Medical Research 1988;87:157‐60. - PubMed
Choo 1994 {published data only}
-
- Choo KE, Oppenheimer SJ, Ismail AB, Ong KH. Rapid serodiagnosis of typhoid fever by dot enzyme immunoassay in an endemic area. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1994;19(1):172‐6. - PubMed
Choo 1997 {published data only}
-
- Choo KE, Davis TME, Ismail A, Ong KH. Longevity of antibody responses to a Salmonella Typhi‐specific outer membrane protein: interpretation of a dot enzyme immunosorbent assay in an area of high typhoid fever endemicity. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1997;57(6):656‐9. - PubMed
Chua 2012 {published data only}
-
- Chua AL, Aziah I, Balaram P, Bhuvanendran S, Anthony AAA, Mohmad SN, et al. Identification of carriers among individuals recruited in the Typhoid Registry in Malaysia using stool culture, polymerase chain reaction, and dot enzyme immunoassay as detection tools. Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health 2012;27(2):NP2740‐8. [DOI: 10.1177/1010539512458521; PUBMED: 23000800] - DOI - PubMed
Coovadia 1986 {published data only}
Das 2013 {published data only}
Dhanalakshmi 1986 {published data only}
-
- Dhanalakshmi D, Mallika M, Kumaravel K, Bhavani M, Lakshminarayana CS. Detection of Salmonella Typhi antigens by slide coagglutination in urine from patients with typhoid fever. Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology 1984;27(1):33‐5. - PubMed
el‐Falaky 1970 {published data only}
-
- el‐Falaky IH, Hassan A, Wahab MF, el‐Kholy S. Diagnosis of Typhoid Fever by Haemagglutination. Journal of the Egyptian Public Health Association 1970;45(1):109‐18. - PubMed
Fadeel 2004 {published data only}
-
- Fadeel MA, Crump JA, Mahoney FJ, Nakhla IA, Mansour AM, Reyad B, et al. Rapid diagnosis of typhoid fever by enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay detection of Salmonella serovar Typhi antigens in urine. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2004;70(3):323‐8. - PubMed
Felezsko 2004 {published data only}
Gorelov 1988 {published data only}
-
- Gorelov AL, Levina GA, Kulyakina MN, Pavlova IP, Shakkanina KL, Prozorovsky SSV. Development and employment of an enzyme immuno‐assay test system for the detection of Salmonella typhi antigens in the blood typhoid fever patient. Laboratornoe Delo 1988;1:79‐83. - PubMed
Handojo 2004 {published data only}
-
- Handojo I, Edijanto SP, Probohoesodo MY, Mahartini NN. Comparison of the diagnostic value of local Widal slide test with imported Widal slide test. South East Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 2004;35(2):366‐70. - PubMed
Hoffman 1986 {published data only}
-
- Hoffman SL, Flanigan TP, Klaucke D, Leksana B, Rockhill RC, Punjabi NH, et al. The Widal slide agglutination test: a valuable rapid diagnostic test in typhoid fever patients at the Infectious Disease Hospital of Jakarta. American Journal of Epidemiology 1986;123(5):869‐75. - PubMed
House 2005 {published data only}
Jackson 1995 {published data only}
-
- Jackson AA, Ismail A, Ibrahim TA, Kader ZS, Nawi NM. Retrospective review of dot enzyme immunoassay test for typhoid fever in an endemic area. South East Asian Journal of Public Health 1995;26(4):625‐30. - PubMed
John 1984 {published data only}
Kalhan 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kalhan R, Kaur I, Singh RP, Gupta HC. Rapid diagnosis of typhoid fever. Indian Journal of Paediatrics 1998;65(4):561‐4. - PubMed
Kalhan 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kalhan R, Kaur I, Singh RP, Gupta HC. Latext agglutination test (LAT) for the diagnosis of typhoid fever. Indian Journal of Paediatrics 1999;36(1):65‐8. - PubMed
Kariuki 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kariuki S, Mwituria J, Munyalo A, Revathi G, Onsongo J. Typhoid is over‐reported in Embu and Nairobi, Kenya. African Journal of Health Science 2004;11(3‐4):103‐10. - PubMed
Kaur 1988a {published data only}
-
- Kaur IR, Talwar V, Gupta HC, Rawat S. Comparative evaluation of latex agglutination (LAT) and coagglutination (COAG) tests for rapid diagnosis of typhoid fever. Journal of Communicable Diseases 1998;20(4):344‐8. [PUBMED: 3268601] - PubMed
Kaur 1988b {published data only}
-
- Kaur I, Talwar V, Rawat S, Anwar M, Gupta HC. Comparison of rapid serodiagnostic tests for antigen detection in typhoid fever. Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology 1998;31(3):245‐7. [PUBMED: 3235132] - PubMed
Khanam 2013 {published data only}
-
- Khanam F, Sheikh A, Sayeed MA, Bhuiyan MS, Choudhury FK, Salma U, et al. Evaluation of a typhoid/paratyphoid diagnostic assay (TPTest) detecting anti‐Salmonella IgA in secretions of peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients in Dhaka, Bangladesh. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 2013;7(7):e2316. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002316] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Khanam 2015 {published data only}
-
- Khanam F, Sayeed MA, Choudhury FK, Sheikh A, Ahmed D, Goswami D, et al. Typhoid fever in young children in Bangladesh: clinical findings, antibiotic susceptibility pattern and immune responses. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 2015;9(4):e0003619. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003619] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Kollaritsch 1988 {published data only}
-
- Kollaritsch H, Hirschl A, Stanek G, Rotter ML. Agglutination test versus ELISA in the diagnosis of typhoid fever. European Journal of Epidemiology 1988;4(1):127‐8. - PubMed
Korbsrisate 1998 {published data only}
-
- Korbsrisate S, Sarasombath S, Praaporn N, Iamkamala P, Hossain M, Mckay S. Detection of IgM antibody against region IV flagellin of Salmonella paratyphi A. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1998;29(4):864‐71. - PubMed
Kuchuloria 2016 {published data only}
-
- Kuchuloria T, Imnadze P, Mamuchishvili N, Chokheli M, Tsertsvadze T, Endeladze M, et al. Hospital‐based surveillance for infectious etiologies among patients with acute febrile illness in Georgia, 2008–2011. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2016;94(1):236‐42. [DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.15-0400] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Lim 1998 {published data only}
Lutterloh 2012 {published data only}
Malik 2001 {published data only}
-
- Malik AS, Malik RH. Typhoid fever in Malaysian children. Medical Journal of Malaysia 2001;56(4):478‐90. - PubMed
Mukherjee 1993 {published data only}
-
- Mukherjee C, Malik A, Khan HM, Malik A. Rapid diagnosis of typhoid fever for coagglutination in an Indian hospital. Journal of Medical Microbiology 1993;39(1):74‐7. - PubMed
Munir 2015 {published data only}
-
- Munir T, Lodhi M, Ali S, Hussain Zaidi SB, Razak S. Early diagnosis of typhoid By PCR for FliC‐d gene of Salmonella Typhi in patients taking antibiotics. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons‐‐Pakistan 2015;25(9):662‐6. - PubMed
Narayanappa 2010 {published data only}
-
- Narayanappa D, Sripathi R, Jagdishkumar K, Rajani HS. Comparative study of dot enzyme immunoassay (Typhidot‐M) and Widal test in the diagnosis of typhoid fever. Indian Pediatrics 2010;47(4):331‐3. - PubMed
Neil 2012 {published data only}
Nguyen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Nguyen NQ, Tapchaisri P, Chongsa‐nguan M, Cao VV, Doan TT, Sakolvaree Y, et al. Diagnosis of enteric fever caused by Salmonella spp. in Vietnam by a monoclonal antibody‐based dot‐blot ELISA. Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology 1997;15(4):205‐12. - PubMed
Ong 1989 {published data only}
-
- Ong LY, Pang T, Lim SH, Tan EL, Puthucheary SD. A simple adherence test for detection of IgM antibodies in typhoid. Journal of Medical Microbiology 1989;29(3):195‐8. - PubMed
Pandya 1995 {published data only}
-
- Pandya M, Pillai P, Deb M. Rapid diagnosis of typhoid fever by detection of Barber protein and Vi antigen of Salmonella serotype Typhi. Journal of Medical Microbiology 1995;43(3):185‐8. - PubMed
Petchclai 1987 {published data only}
Peterson 2010 {published data only}
Preechakasedkit 2012 {published data only}
-
- Preechakasedkit P, Pinwattana K, Dungchai W, Siangproh W, Chaicumpa W, Tongtawe P, et al. Development of a one‐step immunochromatographic strip test using gold nanoparticles for the rapid detection of Salmonella Typhi in human serum. Biosensors & Bioelectronics 2012;31(1):562‐6. [DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2011.10.031] - DOI - PubMed
Rai 1989 {published data only}
-
- Rai GP, Zachariah K, Shrivastava S. Comparative efficacy of indirect haemagglutination test, indirect fluorescent antibody test and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay in serodiagnosis of typhoid fever. Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1989;92(6):431‐4. - PubMed
Shrivastava 2011 {published data only}
-
- Shrivastava B, Shrivastava V, Shrivastava A. Comparative study of diagnostic procedures in Salmonella infection, causative agent of typhoid fever ‐ an overview study. International Research Journal of Pharmacy 2011;2(9):127‐9.
Surachmanto 2011 {published data only}
-
- Surachmanto E. Prevalance of co‐morbidity of asthma acute exacerbation with typhoid fever. European Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2011;66(Suppl 94):141.
Tantivanich 1984 {published data only}
-
- Tantivanich S, Chongsanguan M, Sangpetchsong V, Tharavanij S. A simple and rapid diagnostic test for typhoid fever. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1984;15(3):317‐22. - PubMed
Thevanesam 1992 {published data only}
-
- Thevanesam V. An evaluation of the SAT in the diagnosis of typhoid. Ceylon Medical Journal 1992;37(2):48‐51. - PubMed
Watt 2005 {published data only}
-
- Watt G, Jongsakul K, Ruangvirayuth R, Kantipong P, Silpapojakul K. Short report: prospective evaluation of a multi‐test strip for the diagnoses of scrub and murine typhus, leptospirosis, dengue fever and Salmonella Typhi infection. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2005;72(1):10‐2. - PubMed
West 1989 {published data only}
-
- West B, Richens JE, Howard PF. Evaluation in Papua New Guinea of a urine coagglutination test and a Widal slide agglutination test for rapid diagnosis of typhoid fever. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1989;83(5):715‐7. - PubMed
Wijedoru 2012 {published data only}
Yan 2011 {published data only}
Zaka‐ur‐Rab 2012 {published data only}
Additional references
Abba 2011
Andrews 2015
Baker 2010
Bhutta 2006
Chu 2006
-
- Chu H, Cole SR. Bivariate meta‐analysis of sensitivity and specificity with sparse data: a generalized linear mixed model approach. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(12):1331‐2. - PubMed
Chuang 2009
-
- Chuang CH, Su LH, Perera J, Carlos C, Tan BH, Kumarasinghe G, et al. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enteric serotype Typhi in seven Asian countries. Epidemiology and Infection 2009;137(2):266‐9. - PubMed
Crump 2004
Crump 2014
Darton 2014
Deen 2012
-
- Deen J, Seidlein L, Andersen F, Elle N, White NJ, Lubell Y. Community‐acquired bacterial bloodstream infections in developing countries in South and Southeast Asia: a systematic review. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2012;12(6):480‐7. - PubMed
Gill 2009
-
- Gill GV, Beeching NJ. Typhoid and paratyphoid fevers. Lecture Notes in Tropical Medicine. 6th Edition. West Sussex: Wiley‐Blackwell, 2009:280‐6.
Herberg 2016
Ismail 2006
-
- Ismail TF. Rapid Diagnosis of Typhoid Fever. Indian Journal of Medical Research 2006;123(4):489‐92. - PubMed
Kariuki 2015
Larsson 2008
-
- Larsson M, Kronvall G, Chuc NT, Karlsson I, Lager F, Hanh HD, et al. Antibiotic medication and bacterial resistance to antibiotics: a survey of children in a Vietnamese community. Tropical Medicine & International Health 2008;5(10):711‐21. - PubMed
Maskey 2006
-
- Maskey AP, Day JN, Phung QT, Thwaites GE, Campbell JI, Zimmerman M, Farrar JJ, Basnyat B. Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi A and S. enterica serovar Typhi cause indistinguishable clinical syndromes in Kathmandu, Nepal. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2006;42(9):1247‐53. - PubMed
Massi 2005
-
- Massi MN, Shirakawa T, Gotoh A, Bishnu A, Hatta M, Kawabata M. Quantitative detection of Salmonella enteric serovar Typhi from blood of suspected typhoid fever patients by real‐time PCR. International Journal of Medical Microbiology 2005;295(2):117‐20. - PubMed
McKinnon 2014
Mogasale 2016
Nga 2010
Okeke 2005
-
- Okeke IN, Klugman KP, Bhutta ZA, Duse AG, Jenkins P, O'Brien TF, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in developing countries. Part II: strategies for containment. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2005;5(9):568‐80. - PubMed
Olopoenia 2000
Parry 2002
-
- Parry CM, Hien TT, Dougan G, White NJ, Farrar JJ. Typhoid Fever. New England Journal of Medicine 2002;347(22):1770‐82. - PubMed
Parry 2011
Reddy 2010
Reitsma 2005
-
- Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(10):982‐90. - PubMed
Reitsma 2009
-
- Reitsma JB, Rutjes AWS, Khan KS, Coomarasamy A, Bossuyt PM. A review of solutions for diagnostic accuracy studies with an imperfect or missing reference standard. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2009;62(8):797‐806. - PubMed
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rutter 2001
-
- Rutter CM, Gatsonis CA. A hierarchical regression approach to meta‐analysis of diagnostic test accuracy evaluations. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20(19):2865‐84. - PubMed
Saha 1996
-
- Saha SK, Ruhulamin M, Hanif M, Islam M, Khan WA. Interpretation of the Widal test in the diagnosis of typhoid fever in Bangladeshi children. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics 1996;16(1):75‐8. - PubMed
Shetty 2008
-
- Shetty P. Antibiotic resistance: frequently asked questions. 26 March 2008. www.scidev.net/global/health/feature/antibiotic‐resistance‐frequently‐as... (accessed 10 June 2009).
Smits 2013
Storey 2015
Takwoingi 2013
Thriemer 2013
UNICEF 2006
-
- UNICEF. Progress for Children. A Report Card on Water and Sanitation. Number 6, September 2006. https://www.unicef.org/publications/files/Progress_for_Children_No._5_‐_... (accessed 11 September 2010).
Waddington 2014
Wain 1998
Wain 2001
Whiting 2003
WHO 2003
-
- World Health Organization. Background document: the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of typhoid fever. WHO/V&B/03.07. 2003. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/68122/1/WHO_V‐B_03.07_eng.pdf (accessed 11 September 2010).
WHO 2009
-
- World Health Organization. Evaluation of commercially available anti‐dengue virus immunoglobulin M tests. Diagnostic Evaluation Series No. 3. http://www.who.int/tdr/publications/documents/diagnostics‐evaluation‐3.p.... Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases (accessed 11 September 2010). [ISBN 978 92 4 1597753]
Wilson 1994
-
- Wilson ML. Blood cultures. Introduction. Clinics in Laboratory Medicine 1994;14(1):1‐7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

