The effect of disease severity markers on quality of life in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression
- PMID: 28545401
- PMCID: PMC5445294
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-017-0578-6
The effect of disease severity markers on quality of life in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression
Abstract
Background: Little is known about determinants of quality of life (QoL) in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Recent studies suggest that QoL in ADPKD is determined by more factors than mere renal function. We investigated the effect of ADPKD on QoL and evaluated how Qol is affected by disease severity markers renal function, kidney volume and liver volume.
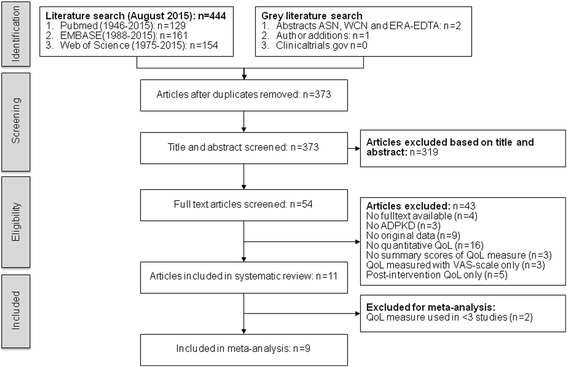
Methods: We performed a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression analyses of cohort studies and randomized controlled trials investigating patient-reported QoL in adult patients with ADPKD not yet on dialysis. EMBASE, MEDLINE, and Web of Science were searched to August 2015 without language restrictions. Two investigators independently reviewed title, abstracts and full text of potentially relevant citations to determine eligibility. We compared pooled QoL summary scores of ADPKD patients using a random-effects meta-analytic model. These scores were compared with mean and age-corrected reference scores of the general population. In a meta-regression analysis, we investigated the univariate effect of renal function, kidney volume and liver volume on QoL.
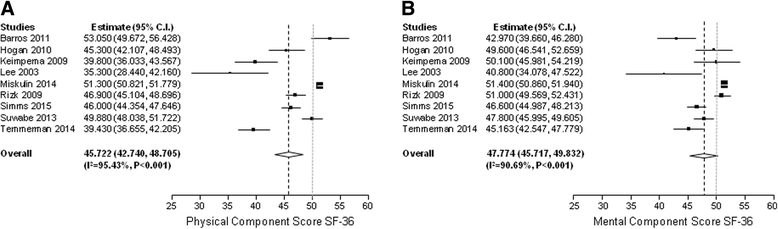
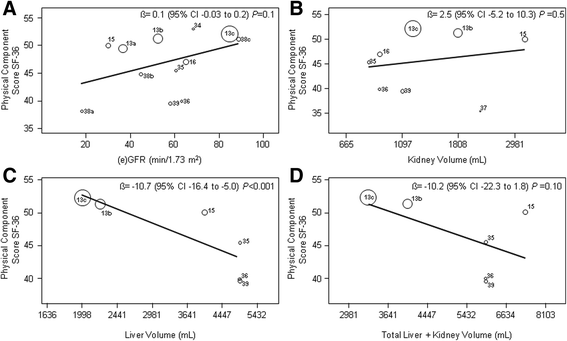
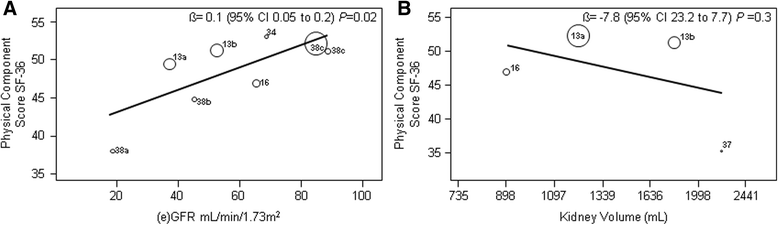
Results: We included nine studies in meta-analysis including 1623 patients who completed the SF-36 questionnaire. Pooled physical (PCS) and mental component scores (MCS) of the SF-36 of individuals with ADPKD were lower than those of the reference population (45.7 vs. 50.0 and 47.8 vs. 50.0 points, both P < 0.001). QoL of ADPKD patients remained lower after comparison with age-corrected reference values (age 35-44 year; PCS 52.2, MCS 49.9 points, both P < 0.05). Larger liver volume negatively impacted PCS (P < 0.001) and MCS (P = 0.001), whereas there was no association with renal function (PCS P = 0.1, MCS P = 0.9) and kidney volume (PCS P = 0.5, MCS P = 0. 5). Total liver and kidney volume had no impact on PCS (P = 0.1), but did have impact on MCS (P = 0.02).
Conclusions: QoL reported by non-dialysis patients with ADPKD is impaired compared to the general population. Large liver volume was the most important factor that diminishes QoL. PROSPERO International Registry number CRD42015026428.
Keywords: Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; Kidney volume; Liver volume; Quality of life; Renal function.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

