Canonical Wnt signaling in diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 28545982
- PMCID: PMC6636823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2017.02.007
Canonical Wnt signaling in diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a common eye complication of diabetes, and the pathogenic mechanism of DR is still under investigation. The canonical Wnt signaling pathway is an evolutionarily conserved pathway that plays fundamental roles in embryogenesis and adult tissue homeostasis. Wnt signaling regulates expression of multiple genes that control retinal development and eye organogenesis, and dysregulated Wnt signaling plays pathophysiological roles in many ocular diseases, including DR. This review highlights recent progress in studies of Wnt signaling in DR. We discuss Wnt signaling regulation in the retina and dysregulation of Wnt signaling associated with ocular diseases with an emphasis on DR. We also discuss the therapeutic potential of modulating Wnt signaling in DR. Continued studies in this field will advance our current understanding on DR and contribute to the development of new treatments.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Diabetes; Inflammation; Oxidative stress; Retinopathy; Wnt signaling.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
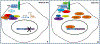
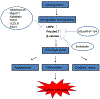
References
-
- Adamiec-Mroczek J, Oficjalska-Mlynczak J, & Misiuk-Hojlo M (2010). Roles of endothelin-1 and selected proinflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of proliferative diabetic retinopathy: Analysis of vitreous samples. Cytokine, 49(3), 269–274. - PubMed
-
- Adamis AP, & Berman AJ (2008). Immunological mechanisms in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Seminars Immunopathology, 30(2), 65–84. - PubMed
-
- Antonetti DA, Barber AJ, Hollinger LA, Wolpert EB, & Gardner TW (1999). Vascular endothelial growth factor induces rapid phosphorylation of tight junction proteins occludin and zonula occluden 1. A potential mechanism for vascular permeability in diabetic retinopathy and tumors. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274(33), 23463–23467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

