The role of IL-6 in neurodevelopment after prenatal stress
- PMID: 28546058
- PMCID: PMC5537020
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.05.015
The role of IL-6 in neurodevelopment after prenatal stress
Abstract
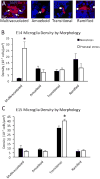
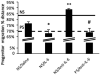
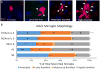
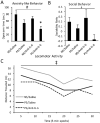
Prenatal stress exposure is associated with adverse psychiatric outcomes, including autism and ADHD, as well as locomotor and social inhibition and anxiety-like behaviors in animal offspring. Similarly, maternal immune activation also contributes to psychiatric risk and aberrant offspring behavior. The mechanisms underlying these outcomes are not clear. Offspring microglia and the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6), known to influence microglia, may serve as common mechanisms between prenatal stress and prenatal immune activation. To evaluate the role of prenatal IL-6 in prenatal stress, microglia morphological analyses were conducted at embryonic days 14 (E14), E15, and in adult mice. Offspring microglia and behavior were evaluated after repetitive maternal restraint stress, repetitive maternal IL-6, or maternal IL-6 blockade during stress from E12 onwards. At E14, novel changes in cortical plate embryonic microglia were documented-a greater density of the mutivacuolated morphology. This resulted from either prenatal stress or IL-6 exposure and was prevented by IL-6 blockade during prenatal stress. Prenatal stress also resulted in increased microglia ramification in adult brain, as has been previously shown. As with embryonic microglia, prenatal IL-6 recapitulated prenatal stress-induced changes in adult microglia. Furthermore, prenatal IL-6 was able to recapitulate the delay in GABAergic progenitor migration caused by prenatal stress. However, IL-6 mechanisms were not necessary for this delay, which persisted after prenatal stress despite IL-6 blockade. As we have previously demonstrated, behavioral effects of prenatal stress in offspring, including increased anxiety-like behavior, decreased sociability, and locomotor inhibition, may be related to these GABAergic delays. While adult microglia changes were ameliorated by IL-6 blockade, these behavioral changes were independent of IL-6 mechanisms, similar to GABAergic delays. This and previous work from our laboratory suggests that multiple mechanisms, including GABAergic delays, may underlie prenatal stress-linked deficits.
Keywords: Embryonic; Gaba; IL-6; Microglia; Prenatal stress.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Additive effects of maternal iron deficiency and prenatal immune activation on adult behaviors in rat offspring.Brain Behav Immun. 2014 Aug;40:27-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.06.005. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Brain Behav Immun. 2014. PMID: 24930842
-
GABAergic modulation with classical benzodiazepines prevent stress-induced neuro-immune dysregulation and behavioral alterations.Brain Behav Immun. 2016 Jan;51:154-168. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Brain Behav Immun. 2016. PMID: 26342944 Free PMC article.
-
Delays in GABAergic interneuron development and behavioral inhibition after prenatal stress.Dev Neurobiol. 2016 Oct;76(10):1078-91. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22376. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Dev Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26724783 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Inflammation and Neurodevelopmental Programming: A Review of Preclinical Outcomes and Implications for Translational Psychiatry.Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Jan 15;85(2):107-121. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.08.008. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30318336 Review.
-
Prenatal Immune and Endocrine Modulators of Offspring's Brain Development and Cognitive Functions Later in Life.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 26;9:2186. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02186. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30319639 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
What Does Immunology Have to Do With Normal Brain Development and the Pathophysiology Underlying Tourette Syndrome and Related Neuropsychiatric Disorders?Front Neurol. 2020 Sep 16;11:567407. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.567407. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33041996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Maternal Exposure to Cypermethrin and Stress Affect Embryonic Brain and Placental Outcomes in Mice.Toxicol Sci. 2020 Jun 1;175(2):182-196. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaa040. Toxicol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32191333 Free PMC article.
-
Differential impact of interleukin-6 promoter gene polymorphism on hippocampal volume in antipsychotic-naïve schizophrenia patients.Indian J Psychiatry. 2020 Jan-Feb;62(1):36-42. doi: 10.4103/psychiatry.IndianJPsychiatry_486_19. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Indian J Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32001929 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress on the mechanism of the impact of maternal childhood trauma on intergenerational transmission].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 15;26(2):207-212. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2309147. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38436321 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
A role for adverse childhood experiences and depression in preeclampsia.J Clin Transl Sci. 2024 Jan 12;8(1):e25. doi: 10.1017/cts.2023.704. eCollection 2024. J Clin Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38384900 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akatsu S, Ishikawa C, Takemura K, Ohtani A, Shiga T. Effects of prenatal stress and neonatal handling on anxiety, spatial learning and serotonergic system of male offspring mice. Neurosci Res. 2015;101:15–23. - PubMed
-
- Antonson AM, Radlowski EC, Lawson MA, Rytych JL, Johnson RW. Maternal viral infection during pregnancy elicits anti-social behavior in neonatal piglet offspring independent of postnatal microglial cell activation. Brain Behav Immun 2016 - PubMed
-
- Antony JM, Paquin A, Nutt SL, Kaplan DR, Miller FD. Endogenous microglia regulate development of embryonic cortical precursor cells. J Neurosci Res. 2011;89:286–298. - PubMed
-
- Avellino AM, Hart D, Dailey AT, MacKinnon M, Ellegala D, Kliot M. Differential macrophage responses in the peripheral and central nervous system during wallerian degeneration of axons. Exp Neurol. 1995;136:183–198. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

