Targeting nuclear receptors for the treatment of fatty liver disease
- PMID: 28546081
- PMCID: PMC6659998
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.05.011
Targeting nuclear receptors for the treatment of fatty liver disease
Abstract
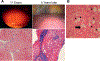
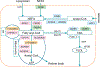
Ligand-activated nuclear receptors, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), pregnane X receptor, and constitutive androstane receptor, were first identified as key regulators of the responses against chemical toxicants. However, numerous studies using mouse disease models and human samples have revealed critical roles for these receptors and others, such as PPARβ/δ, PPARγ, farnesoid X receptor (FXR), and liver X receptor (LXR), in maintaining nutrient/energy homeostasis in part through modulation of the gut-liver-adipose axis. Recently, disorders associated with disrupted nutrient/energy homeostasis, e.g., obesity, metabolic syndrome, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), are increasing worldwide. Notably, in NAFLD, a progressive subtype exists, designated as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) that is characterized by typical histological features resembling alcoholic steatohepatitis (ASH), and NASH/ASH are recognized as major causes of hepatitis virus-unrelated liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Since hepatic steatosis is basically caused by an imbalance between fat/energy influx and utilization, abnormal signaling of these nuclear receptors contribute to the pathogenesis of fatty liver disease. Standard therapeutic interventions have not been fully established for fatty liver disease, but some new agents that activate or inhibit nuclear receptor signaling have shown promise as possible therapeutic targets. In this review, we summarize recent findings on the roles of nuclear receptors in fatty liver disease and discuss future perspectives to develop promising pharmacological strategies targeting nuclear receptors for NAFLD/NASH.
Keywords: Energy vector; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Liver fibrosis; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; Steatohepatitis; Tissue-specific agonist/antagonist.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
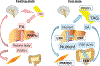
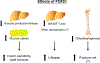
References
-
- Ahn SB, Jang K, Jun DW, Lee BH, & Shin KJ (2014). Expression of liver X receptor correlates with intrahepatic inflammation and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 59(12), 2975–2982. - PubMed
-
- Altmann R, Hausmann M, Spöttl T, Gruber M, Bull AW, Menzel K, … Rogler G (2007). 13-Oxo-ODE is an endogenous ligand for PPARgamma in human colonic epithelial cells. Biochemical Pharmacology 74(4), 612–622. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SP, Dunn C, Laughter A, Yoon L, Swanson C, Stulnig TM, … Corton JC (2004). Overlapping transcriptional programs regulated by the nuclear receptors peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, retinoid X receptor, and liver X receptor in mouse liver. Molecular Pharmacology 66(6), 1440–1452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

