Cross-talk between the H3K36me3 and H4K16ac histone epigenetic marks in DNA double-strand break repair
- PMID: 28546430
- PMCID: PMC5512086
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.788224
Cross-talk between the H3K36me3 and H4K16ac histone epigenetic marks in DNA double-strand break repair
Abstract
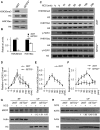
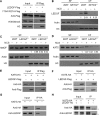
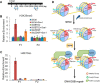
Post-translational modifications of histone proteins regulate numerous cellular processes. Among these modifications, trimethylation of lysine 36 in histone H3 (H3K36me3) and acetylation of lysine 16 in histone H4 (H4K16ac) have important roles in transcriptional regulation and DNA damage response signaling. However, whether these two epigenetic histone marks are mechanistically linked remains unclear. Here we discovered a new pathway through which H3K36me3 stimulates H4K16ac upon DNA double-strand break (DSB) induction in human cells. In particular, we examined, using Western blot analysis, the levels of H3K36me3 and H4K16ac in cells after exposure to various DSB-inducing agents, including neocarzinostatin, γ rays, and etoposide, and found that H3K36me3 and H4K16ac were both elevated in cells upon these treatments. We also observed that DSB-induced H4K16 acetylation was abolished in cells upon depletion of the histone methyltransferase gene SET-domain containing 2 (SETD2) and the ensuing loss of H3K36me3. Furthermore, the H3K36me3-mediated increase in H4K16ac necessitated lens epithelium-derived growth factor p75 splicing variant (LEDGF), which is a reader protein of H3K36me3, and the KAT5 (TIP60) histone acetyltransferase. Mechanistically, the chromatin-bound LEDGF, through its interaction with KAT5, promoted chromatin localization of KAT5, thereby stimulating H4K16 acetylation. In this study, we unveiled cross-talk between two important histone epigenetic marks and defined the function of this cross-talk in DNA DSB repair.
Keywords: DNA repair; epigenetics; histone acetylation; histone methylation; posttranslational modification (PTM).
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

Similar articles
-
The SETD2 Methyltransferase Supports Productive HPV31 Replication through the LEDGF/CtIP/Rad51 Pathway.J Virol. 2023 May 31;97(5):e0020123. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00201-23. Epub 2023 May 8. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37154769 Free PMC article.
-
Selective binding of the PHD6 finger of MLL4 to histone H4K16ac links MLL4 and MOF.Nat Commun. 2019 May 24;10(1):2314. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10324-8. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31127101 Free PMC article.
-
MOF and histone H4 acetylation at lysine 16 are critical for DNA damage response and double-strand break repair.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;30(14):3582-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01476-09. Epub 2010 May 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20479123 Free PMC article.
-
Role of histone acetyltransferases MOF and Tip60 in genome stability.DNA Repair (Amst). 2021 Nov;107:103205. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103205. Epub 2021 Aug 8. DNA Repair (Amst). 2021. PMID: 34399315 Review.
-
Histone acetylation and methylation: combinatorial players for transcriptional regulation.Subcell Biochem. 2007;41:351-69. Subcell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17484136 Review.
Cited by
-
The Implication of Topoisomerase II Inhibitors in Synthetic Lethality for Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 9;16(1):94. doi: 10.3390/ph16010094. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional Repression of Ferritin Light Chain Increases Ferroptosis Sensitivity in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 26;9:719187. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.719187. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34765600 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding histone H3 lysine 36 methylation and its deregulation in disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Aug;76(15):2899-2916. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03144-y. Epub 2019 May 30. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31147750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SETD2: from chromatin modifier to multipronged regulator of the genome and beyond.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jun 6;79(6):346. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04352-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35661267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arsenite Binds to the Zinc Finger Motif of TIP60 Histone Acetyltransferase and Induces Its Degradation via the 26S Proteasome.Chem Res Toxicol. 2017 Sep 18;30(9):1685-1693. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.7b00146. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Chem Res Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28837777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou V. W., Goren A., and Bernstein B. E. (2011) Charting histone modifications and the functional organization of mammalian genomes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 12, 7–18 - PubMed
-
- Suganuma T., and Workman J. L. (2011) Signals and combinatorial functions of histone modifications. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 80, 473–499 - PubMed
-
- Smeenk G., and van Attikum H. (2013) The chromatin response to DNA breaks: leaving a mark on genome integrity. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 82, 55–80 - PubMed
-
- Varier R. A., and Timmers H. T. (2011) Histone lysine methylation and demethylation pathways in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1815, 75–89 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

