Pazopanib for the Treatment of Non-clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase II Study
- PMID: 28546525
- PMCID: PMC5912146
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2016.584
Pazopanib for the Treatment of Non-clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase II Study
Abstract
Purpose: The optimal treatment strategy for patients with metastatic non-clear cell type renal cell carcinoma (nccRCC) remains unclear. Although several inhibitors of vascular endothelial growth factor have recently shown efficacy against nccRCC, the clinical benefit of pazopanib in nccRCC has not been analyzed. We therefore designed a single-arm, open-label, phase II study to determine the efficacy and safety of pazopanib in patients with nccRCC.
Materials and methods: Patientswith locally advanced or metastatic nccRCC, exceptfor collecting duct or sarcomatoid type, received 800 mg/day of pazopanib daily until progression of disease or intolerable toxicity. One cyclewas defined as 4weeks and tumorresponsewas evaluated every two cycles. The primary objective was overall response rate (ORR).
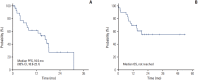
Results: A total of 29 eligible patients were enrolled at nine centers in Korea from December 2012 and September 2014. The median age of the patients was 58 years (range, 27 to 76 years) and 21 patients (72%) were male. Regarding histology type, 19 patients had papillary, three had chromophobe, two had unclassified and five had unknown non-clear cell type. Of 28 evaluable patients, eight achieved a confirmed partial response with ORR of 28%. The median progression-free survival was 16.5 months (95% confidence interval, 10.9 to 22.1) and median overall survival was not reached. Sixteen patients (55%) experienced treatment-related toxicity of grade 3 or more, but most adverse events were overcome through dose reduction and delay.
Conclusion: In this prospective phase II study, pazopanib demonstrated promising activity and tolerable safety profile in patients with metastatic nccRCC.
Keywords: Non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma; Pazopanib; Phase II study.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures
References
-
- Leibovich BC, Lohse CM, Crispen PL, Boorjian SA, Thompson RH, Blute ML, et al. Histological subtype is an independent predictor of outcome for patients with renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2010;183:1309–15. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Bacik J, Mariani T, Russo P, Mazumdar M, Reuter V. Treatment outcome and survival associated with metastatic renal cell carcinoma of non-clear-cell histology. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:2376–81. - PubMed
-
- Vera-Badillo FE, Templeton AJ, Duran I, Ocana A, de Gouveia P, Aneja P, et al. Systemic therapy for non-clear cell renal cell carcinomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol. 2015;67:740–9. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network . Fort Washington, PA: National Comprehensive Cancer Network; 2016. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology, kidney cancer. version 2. 2016 [Internet] [cited 2016 Oct 20]. Available from: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf. - PubMed
-
- Dutcher JP, de Souza P, McDermott D, Figlin RA, Berkenblit A, Thiele A, et al. Effect of temsirolimus versus interferon-alpha on outcome of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma of different tumor histologies. Med Oncol. 2009;26:202–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources