Melatonin-mediated mitophagy protects against early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- PMID: 28546552
- PMCID: PMC5445068
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02679-z
Melatonin-mediated mitophagy protects against early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Melatonin-mediated mitophagy protects against early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 18;14(1):21823. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71815-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39294188 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
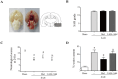
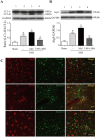
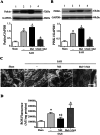
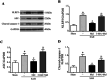
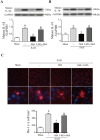
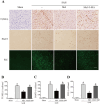
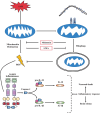
The NLRP3 inflammasome is activated in the early period following subarachnoid hemorrhage(SAH), resulting in inflammatory responses. Recent studies have shown that activation of NLRP3 inflammasome is suppressed by autophagy, but the potential mechanism is unclear. In this study, we examined whether mitophagy was involved in the beneficial effect of melatonin and its relationship with NLRP3 inflammasome activation after SAH. In total, 130 adult-male SD rats were randomly divided into four groups: sham group, SAH + vehicle group, SAH + melatonin group, and SAH + 3-methyladenine (3-MA) + melatonin group. Brain samples were used for brain water content analysis, ROS assay, Western blot, immunohistochemistry and transmission electron microscopy. The results showed that melatonin treatment markedly increased the expression of both autophagy markers(LC3-II/LC3-I and Atg 5), and mitophagy markers(Parkin and PINK-1) following SAH induction. Additionally, melatonin treatment attenuated pathological changes in mitochondria and reduced ROS generation, which are closely related to NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Consequently, melatonin-mediated upregulation of proteins associated with mitophagy inhibited NLRP3 inflammasome activation and significantly reduced pro-inflammatory cytokine levels after SAH. Conversely, 3-MA, an autophagy inhibitor, reversed these beneficial effects of melatonin on mitophagy and the NLRP3 inflammasome. These results suggest that mitophagy-associated NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition by melatonin is neuroprotective against early brain injury post-SAH in rats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Connolly, E. S. Jr. et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american Stroke Association. Stroke43, 1711–1737, doi:10.1161/STR.0b013e3182587839 (2012). 10.1161/STR.0b013e3182587839 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dumont, A. S. et al. Cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: putative role of inflammation. Neurosurgery53, 123–133, discussion 133–125 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

