Reduced GABAergic neuronal activity in zona incerta causes neuropathic pain in a rat sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury model
- PMID: 28546770
- PMCID: PMC5436785
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S131104
Reduced GABAergic neuronal activity in zona incerta causes neuropathic pain in a rat sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury model
Abstract
Purpose: The zona incerta (ZI) is below the ventral tier of the thalamus and has a strong influence selectively in higher-order thalamic relays. Although neuropathic pain has been suggested to result from reduced gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and GABAergic signaling in the ZI, the mechanisms remain unclear. Here, the role of GABA and GABAergic signaling was investigated in the ZI in neuropathic pain using sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury (CCI) rats.
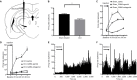
Materials and methods: Single-unit neuronal activity was recorded, and microdialysis was performed in the ZI of CCI rats and sham-treated rats in vivo. This study also compared ZI neuronal activity after treatment with saline, the GABAA receptor agonist (muscimol), or the GABAA receptor antagonist (bicuculline).
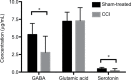
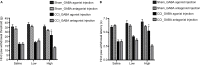
Results and conclusion: CCI rats exhibited hypersensitivity to pain as evidenced by decreased hind paw withdrawal threshold and latency. CCI rats also showed reduced GABA level and decreased neuronal activity in the ZI compared with sham-treated rats. Treatment with GABAA receptor agonist, but not GABAA receptor antagonist, ameliorated pain hypersensitivity and increased the firing rate (spikes/s) of ZI neurons in CCI rats.
Keywords: GABA; chronic pain; neural cell recording; neuropathic pain; sciatic nerve injury; zona incerta.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Jung BF, Ahrendt GM, Oaklander AL, Dworkin RH. Neuropathic pain following breast cancer surgery: proposed classification and research update. Pain. 2003;104(1–2):1–13. - PubMed
-
- Schmader KE. Epidemiology and impact on quality of life of postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy. Clin J Pain. 2002;18(6):350–354. - PubMed
-
- Raskin J, Pritchett YL, Wang F, et al. A double-blind, randomized multicenter trial comparing duloxetine with placebo in the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain Med. 2005;6(5):346–356. - PubMed
-
- Heitmann H, Biberacher V, Tiemann L, et al. Prevalence of neuropathic pain in early multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2016;22(9):1224–1230. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

