Effectiveness of a participatory eye care program in reducing eye strain among staff computer users in Thailand
- PMID: 28546777
- PMCID: PMC5436759
- DOI: 10.2147/RMHP.S134940
Effectiveness of a participatory eye care program in reducing eye strain among staff computer users in Thailand
Abstract
Background: The increased usage of computers results in a variety of health problems, particularly eye strain, which is the most common workplace complaint today.
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a participatory eye care (PEC) program by comparing eye care knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP), as well as eye strain symptoms in staff computer users at Sukhothai Thammathirat Open University, Thailand.
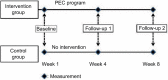
Methods: A participatory approach was held by organizing a meeting of 26 stakeholders to get opinions for developing the PEC program. The developed PEC program consisted of 3-hour training course on eye strain, rest breaks for 30 seconds every 30 minutes of computer use, and 15-minute rest break (in the morning and the afternoon) with integrated eye-neck exercises. Then, a quasi-experiment was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the PEC program. A total of 35 staff computer users enrolled in each of intervention and control groups for 8 weeks. Chi-square test and repeated measures analysis of variance were used for comparison of eye strain symptoms and the KAP scores.
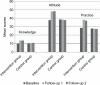
Results: The intervention was associated with reduction in percentage of eye strain. Significant differences were found between the intervention and the control groups at follow-up 1 (χ2=18.529, p-value <0.001) and follow-up 2 (χ2=18.651, p-value <0.001). The PEC program likely increased the beneficial effect on KAP scores between the groups and between times (p<0.05).
Conclusion: The findings currently provide evidence to support a practical program developed through a participatory approach, which both researchers and computer users could apply to reduce eye strain.
Keywords: computer users; eye strain; participatory program.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Erratum.Mult Scler. 2016 Oct;22(12):NP9-NP11. doi: 10.1177/1352458515585718. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Mult Scler. 2016. PMID: 26041800
-
Lifestyle Change Plus Dental Care (LCDC) program improves knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) toward oral health and diabetes mellitus among the elderly with type 2 diabetes.J Med Assoc Thai. 2015 Mar;98(3):279-90. J Med Assoc Thai. 2015. PMID: 25920299 Clinical Trial.
-
Changes in postural risk and general health associated with a participatory ergonomics education program used by heavy video display terminal users: a pilot study.J Hand Ther. 2003 Jan-Mar;16(1):29-35. doi: 10.1016/s0894-1130(03)80021-2. J Hand Ther. 2003. PMID: 12611443
-
Process evaluation of a National Primary Eye Care Programme in Rwanda.BMC Health Serv Res. 2018 Dec 7;18(1):950. doi: 10.1186/s12913-018-3718-1. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018. PMID: 30526579 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Factors which Contribute to the Ocular Complaints in Computer Users.J Clin Diagn Res. 2013 Feb;7(2):331-5. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2013/5150.2760. Epub 2012 Dec 24. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013. PMID: 23543722 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Interventional Study on the Effectiveness of Eye Exercises Based on Composite Feedback Model in School-Age Children.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024 Jul 8;17:1787-1801. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S467570. eCollection 2024. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024. PMID: 39007108 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of computer workstations ergonomics and its relationship with reported musculoskeletal and visual symptoms among university employees in Jordan.Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2022 Apr 11;35(2):141-156. doi: 10.13075/ijomeh.1896.01822. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2022. PMID: 34605825 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the impact of the exercise package on eye and neck strain (EPENS) among adolescents: A pre-experimental study at a selected preuniversity college in Mangalore.J Educ Health Promot. 2024 Nov 29;13:459. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_20_24. eCollection 2024. J Educ Health Promot. 2024. PMID: 39811866 Free PMC article.
-
Low Vision Rehabilitation and Eye Exercises: A Comprehensive Guide to Tertiary Prevention of Diabetic Retinopathy.Life (Basel). 2025 May 26;15(6):857. doi: 10.3390/life15060857. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40566511 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khalaj M, Ebrahimi M, Shojai P, Bagherzadeh R, Sadeghi T, Ghalenoei M. Computer vision syndrome in eleven to eighteen-year-old students in Qazvin. Biotech Health Sci. 2015;2(3):e28234.
-
- Atencio R. Eyestrain: the number one complaint of computer users. Comput Libr. 1996;16(8):40–44.
-
- Sullivan JM. Visual Fatigue and the Driver. Ann Arbor: The University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute; 2008. pp. 2–6.
-
- ICD10 Data.com [webpage on the Internet] Unspecified subjective visual disturbances. 2016. [Accessed February 5, 2017]. [cited November 24, 2016]. Available from: http://www.icd10data.com/ICD10CM/Codes/H00-H59/H53-H54/H53-/H53.10.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

