The Repeated Administration of Resveratrol Has Measurable Effects on Circulating T-Cell Subsets in Humans
- PMID: 28546852
- PMCID: PMC5435979
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/6781872
The Repeated Administration of Resveratrol Has Measurable Effects on Circulating T-Cell Subsets in Humans
Abstract
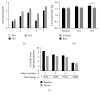
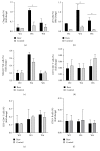
Preclinical studies have shown that resveratrol exerts immunomodulatory effects with potential clinical value in the amelioration of autoimmune disorders and cancer prevention; however, little is known about the in vivo effects of this naturally occurring polyphenol on human immune cells. We assessed the effects of repeated doses of resveratrol (1000 mg/day for 28 days) on circulating immune cells in healthy Japanese individuals. Resveratrol was safe and well tolerated and was associated with significant increases in the numbers of circulating γδ T cells and regulatory T cells and resulted in small, yet significant, decreases in the plasma levels of the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and MCP-1 and a significant increase in the plasma antioxidant activity compared with the corresponding antioxidant baseline activity and with that in four control individuals. In in vitro studies, resveratrol significantly improved the growth of γδ T cells and regulatory T cells. These findings demonstrate that resveratrol has some clear biological effects on human circulating immune cells. Further studies are necessary to interpret the long-term immunological changes associated with resveratrol treatment.
Figures



References
-
- Patel K. R., Scott E., Brown V. A., Gescher A. J., Steward W. P., Brown K. Clinical trials of resveratrol. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2011;1215(1):161–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

