Chloroquine inhibits Ca2+ permeable ion channels-mediated Ca2+ signaling in primary B lymphocytes
- PMID: 28546857
- PMCID: PMC5442594
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-017-0155-5
Chloroquine inhibits Ca2+ permeable ion channels-mediated Ca2+ signaling in primary B lymphocytes
Abstract
Background: Chloroquine, a bitter tastant, inhibits Ca2+ signaling, resulting in suppression of B cell activation; however, the inhibitory mechanism remains unclear.
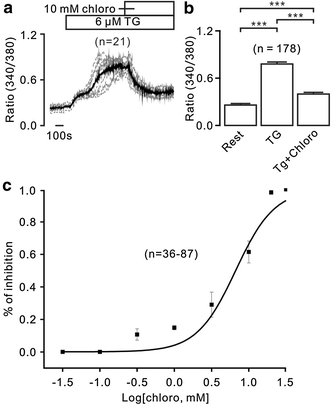
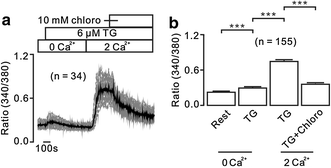
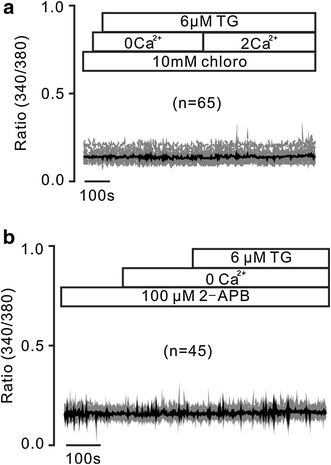
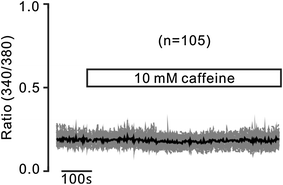
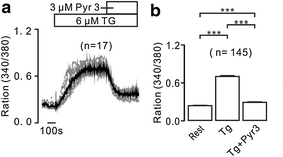
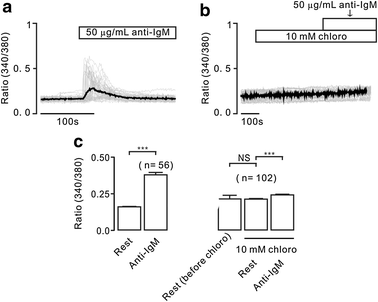
Results: In this study, thapsigargin (TG), but not caffeine, induced sustained intracellular Ca2+ increases in mouse splenic primary B lymphocytes, which were markedly inhibited by chloroquine. Under Ca2+-free conditions, TG elicited transient Ca2+ increases, which additionally elevated upon the restoration of 2 mM Ca2+. The former were from release of intracellular Ca2+ store and the latter from Ca2+ influx. TG-induced release was inhibited by 2-APB (an inhibitor of inositol-3-phosphate receptors, IP3Rs) and chloroquine, and TG-caused influx was inhibited by pyrazole (Pyr3, an inhibitor of transient receptor potential C3 (TRPC3) and stromal interaction molecule (STIM)/Orai channels) and chloroquine. Moreover, chloroquine also blocked Ca2+ increases induced by the engagement of B cell receptor (BCR) with anti-IgM.
Conclusions: These results indicate that chloroquine inhibits Ca2+ elevations in splenic B cells through inhibiting Ca2+ permeable IP3R and TRPC3 and/or STIM/Orai channels. These findings suggest that chloroquine would be a potent immunosuppressant.
Keywords: B cells; Ca2+; Chloroquine; IP3R; STIM/Orai channels; TRPC3 channels.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chloroquine Inhibits Ca(2+) Signaling in Murine CD4(+) Thymocytes.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(1):133-40. doi: 10.1159/000374058. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25925287
-
Modification of phospholipase C-gamma-induced Ca2+ signal generation by 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate.Biochem J. 2003 Dec 15;376(Pt 3):667-76. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031345. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 14558886 Free PMC article.
-
STIM-1 and ORAI-1 channel mediate angiotensin-II-induced expression of Egr-1 in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Dec;232(12):3496-3509. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25810. Epub 2017 Feb 21. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28105751
-
Altered expression of stromal interaction molecule (STIM)-calcium release-activated calcium channel protein (ORAI) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP3Rs) in cancer: will they become a new battlefield for oncotherapy?Chin J Cancer. 2016 Mar 24;35:32. doi: 10.1186/s40880-016-0094-2. Chin J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27013185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Basis and Regulation of Store-Operated Calcium Entry.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1131:445-469. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-12457-1_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31646520 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic deletion of the Tas2r143/Tas2r135/Tas2r126 cluster reveals that TAS2Rs may not mediate bitter tastant-induced bronchodilation.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Sep;236(9):6407-6423. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30315. Epub 2021 Feb 8. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33559206 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial peptide LL-37 increases rhinovirus-induced interferon β expression in human airway epithelial cells through a Ca2+-dependent mechanism.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Jun 21;43:102105. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102105. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40612001 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Lysosomal Stress on Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Derived Schwann Cells.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 27;14(4):405. doi: 10.3390/biom14040405. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672423 Free PMC article.
-
Various Aspects of Calcium Signaling in the Regulation of Apoptosis, Autophagy, Cell Proliferation, and Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 6;21(21):8323. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218323. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33171939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chloroquine to fight COVID-19: A consideration of mechanisms and adverse effects?Heliyon. 2020 Sep;6(9):e04900. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04900. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32935064 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

