Ocular penetration of topically applied 1% tigecycline in a rabbit model
- PMID: 28546920
- PMCID: PMC5437451
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2017.05.03
Ocular penetration of topically applied 1% tigecycline in a rabbit model
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate ocular penetration of topically applied 1% tigecycline.
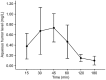
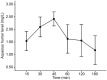
Methods: Forty-two New Zealand White rabbits were divided into 3 groups. A 50 µL drop of 1% tigecycline was administered in group 1. In groups 2 and 3, the drop was administered every 15min for 60min (keratitis protocol). Aqueous humor samples in groups 1 and 2 were collected under general anesthesia at 15, 30, 45, 60, 120, and 180min after the last drop. All animals in group 3 were euthanatized. Cornea, vitreous and blood samples were collected 60 and 120min after the last drop. Tigecycline concentrations were measured using high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).
Results: The peak aqueous humor tigecycline concentration [mean 0.73±0.14 mg/L (SD) and 2.41±0.14 mg/L, respectively] occurred 45min after topical drug application in groups 1 and 2. Group 3 mean values in the cornea, and vitreous, were 3.27±0.50 µg/g, and 0.17±0.10 mg/L at 60min and 3.17±0.77 µg/g and 0.20±0.07 mg/L at 120min, respectively. Tigecycline serum concentrations were negligible.
Conclusion: Tigecycline levels in the aqueous humor in groups 1 and 2, and in the cornea in group 3 exceeded the minimum inhibitory concentrations of most gram-positive organisms that cause bacterial keratitis and endophthalmitis.
Keywords: antibiotic; aqueous humor; cornea; pharmacokinetics; rabbit eyes.
Figures
References
-
- Green M, Apel A, Stapleton F. Risk factors and causative organisms in microbial keratitis. Cornea. 2008;27(1):22–27. - PubMed
-
- Ly CN, Pham JN, Badenoch PR, Bell SM, Hawkins G, Rafferty DL, McClellan KA. Bacteria commonly isolated from keratitis specimens retain antibiotic susceptibility to fluoroquinolones and gentamicin plus cephalothin. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006;34(1):44–50. - PubMed
-
- Scoper SV. Review of third- and fourth-generation fluoroquinolones in ophthalmology: in vitro and in vivo efficacy. Adv Ther. 2008;25(10):979–994. - PubMed
-
- McDonald M, Blondeau JM. Emerging antibiotic resistance in ocular infections and the role of fluoroquinolones. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36(9):1588–1598. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources