Car8 dorsal root ganglion expression and genetic regulation of analgesic responses are associated with a cis-eQTL in mice
- PMID: 28547032
- PMCID: PMC5693610
- DOI: 10.1007/s00335-017-9694-7
Car8 dorsal root ganglion expression and genetic regulation of analgesic responses are associated with a cis-eQTL in mice
Abstract
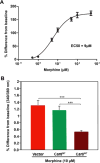
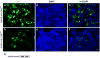
Carbonic anhydrase-8 (Car8 mouse gene symbol) is devoid of enzymatic activity, but instead functions as an allosteric inhibitor of inositol trisphosphate receptor-1 (ITPR1) to regulate this intracellular calcium release channel important in synaptic functions and neuronal excitability. Causative mutations in ITPR1 and carbonic anhydrase-8 in mice and humans are associated with certain subtypes of spinal cerebellar ataxia (SCA). SCA mice are genetically deficient in dorsal root ganglia (DRG) Car8 expression and display mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity and susceptibility to subacute and chronic inflammatory pain behaviors. In this report, we show that DRG Car8 expression is variable across 25 naïve-inbred strains of mice, and this cis-regulated eQTL (association between rs27660559, rs27706398, and rs27688767 and DRG Car8 expression; P < 1 × 10-11) is correlated with nociceptive responses in mice. Next, we hypothesized that increasing DRG Car8 gene expression would inhibit intracellular calcium release required for morphine antinociception and might correlate with antinociceptive sensitivity of morphine and perhaps other analgesic agents. We show that mean DRG Car8 gene expression is directly related to the dose of morphine or clonidine needed to provide a half-maximal analgesic response (r = 0.93, P < 0.00002; r = 0.83, P < 0.0008, respectively), suggesting that greater DRG Car8 expression increases analgesic requirements. Finally, we show that morphine induces intracellular free calcium release using Fura 2 calcium imaging in a dose-dependent manner; V5-Car8 WT overexpression in NBL cells inhibits morphine-induced calcium increase. These findings highlight the 'morphine paradox' whereby morphine provides antinociception by increasing intracellular free calcium, while Car8 and other antinociceptive agents work by decreasing intracellular free calcium. This is the first study demonstrating that biologic variability associated with this cis-eQTL may contribute to differing analgesic responses through altered regulation of ITPR1-dependent calcium release in mice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Profound analgesia is associated with a truncated peptide resulting from tissue specific alternative splicing of DRG CA8-204 regulated by an exon-level cis-eQTL.PLoS Genet. 2019 Jun 14;15(6):e1008226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008226. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31199789 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic anhydrase-8 regulates inflammatory pain by inhibiting the ITPR1-cytosolic free calcium pathway.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 3;10(3):e0118273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118273. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25734498 Free PMC article.
-
Human carbonic anhydrase-8 AAV8 gene therapy inhibits nerve growth factor signaling producing prolonged analgesia and anti-hyperalgesia in mice.Gene Ther. 2018 Jul;25(4):297-311. doi: 10.1038/s41434-018-0018-7. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Gene Ther. 2018. PMID: 29789638 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of human CA8 on thermal antinociception in relation to morphine equivalence in mice.Neuroreport. 2017 Dec 13;28(18):1215-1220. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000872. Neuroreport. 2017. PMID: 28902707 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium Signaling, PKC Gamma, IP3R1 and CAR8 Link Spinocerebellar Ataxias and Purkinje Cell Dendritic Development.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018 Jan 30;16(2):151-159. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170529104000. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28554312 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
rdHSV-CA8 non-opioid analgesic gene therapy decreases somatosensory neuronal excitability by activating Kv7 voltage-gated potassium channels.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 May 9;17:1398839. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1398839. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38783904 Free PMC article.
-
Profound analgesia is associated with a truncated peptide resulting from tissue specific alternative splicing of DRG CA8-204 regulated by an exon-level cis-eQTL.PLoS Genet. 2019 Jun 14;15(6):e1008226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008226. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31199789 Free PMC article.
-
Next-generation replication-defective HSV vectors for delivery of large DNA payloads.Mol Ther. 2025 May 7;33(5):2205-2216. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.03.055. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40181547 Review.
-
Zhx2 Is a Candidate Gene Underlying Oxymorphone Metabolite Brain Concentration Associated with State-Dependent Oxycodone Reward.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2022 Aug;382(2):167-180. doi: 10.1124/jpet.122.001217. Epub 2022 Jun 10. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2022. PMID: 35688478 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-modifying rdHSV-CA8* non-opioid analgesic gene therapy treats chronic osteoarthritis pain by activating Kv7 voltage-gated potassium channels.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Jul 17;17:1416148. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1416148. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39086927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoki T, Narita M, Ohnishi O, Mizuo K, Narita M, Yajima Y, Suzuki T. Disruption of the type 1 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor gene suppresses the morphine-induced antinociception in the mouse. Neuroscience Letters. 2003;350:69–72. - PubMed
-
- Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:3440–3450. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

