Flavonoids: promising natural compounds against viral infections
- PMID: 28547385
- PMCID: PMC7087220
- DOI: 10.1007/s00705-017-3417-y
Flavonoids: promising natural compounds against viral infections
Abstract
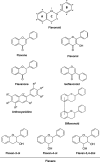
Flavonoids are widely distributed as secondary metabolites produced by plants and play important roles in plant physiology, having a variety of potential biological benefits such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral activity. Different flavonoids have been investigated for their potential antiviral activities and several of them exhibited significant antiviral properties in in vitro and even in vivo studies. This review summarizes the evidence for antiviral activity of different flavonoids, highlighting, where investigated, the cellular and molecular mechanisms of action on viruses. We also present future perspectives on therapeutic applications of flavonoids against viral infections.
Conflict of interest statement
This study is supported by the RA MES State Committee of Science, in the frames of the research projects 15RF-081 and 16YR-1F064. All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmadi A, Hassandarvish P, Lani R, Yadollahi P, Jokar A, Bakar SA, Zandi K. Inhibition of chikungunya virus replication by hesperetin and naringenin. RSC Adv. 2016;6:69421–69430. doi: 10.1039/C6RA16640G. - DOI
-
- Bachmetov L, Gal-Tanamy M, Shapira A, Vorobeychik M, Giterman-Galam T, Sathiyamoorthy P, Golan-Goldhirsh A, Benhar I, Tur-Kaspa R, Zemel R. Suppression of hepatitis C virus by the flavonoid quercetin is mediated by inhibition of NS3 protease activity. J Viral Hepat. 2012;19(2):e81–e88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01507.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical