HGF-Met Pathway in Regeneration and Drug Discovery
- PMID: 28548072
- PMCID: PMC5344275
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines2040275
HGF-Met Pathway in Regeneration and Drug Discovery
Abstract
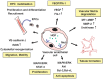
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is composed of an α-chain and a β-chain, and these chains contain four kringle domains and a serine protease-like structure, respectively. Activation of the HGF-Met pathway evokes dynamic biological responses that support morphogenesis (e.g., epithelial tubulogenesis), regeneration, and the survival of cells and tissues. Characterizations of conditional Met knockout mice have indicated that the HGF-Met pathway plays important roles in regeneration, protection, and homeostasis in various cells and tissues, which includes hepatocytes, renal tubular cells, and neurons. Preclinical studies designed to address the therapeutic significance of HGF have been performed on injury/disease models, including acute tissue injury, chronic fibrosis, and cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. The promotion of cell growth, survival, migration, and morphogenesis that is associated with extracellular matrix proteolysis are the biological activities that underlie the therapeutic actions of HGF. Recombinant HGF protein and the expression vectors for HGF are biological drug candidates for the treatment of patients with diseases and injuries that are associated with impaired tissue function. The intravenous/systemic administration of recombinant HGF protein has been well tolerated in phase I/II clinical trials. The phase-I and phase-I/II clinical trials of the intrathecal administration of HGF protein for the treatment of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and spinal cord injury, respectively, are ongoing.
Keywords: HGF; Met; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; clinical trial; spinal cord injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
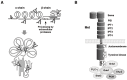
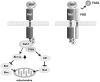

Similar articles
-
Biological roles of hepatocyte growth factor-Met signaling from genetically modified animals.Biomed Rep. 2017 Dec;7(6):495-503. doi: 10.3892/br.2017.1001. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Biomed Rep. 2017. PMID: 29188052 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor and Met in drug discovery.J Biochem. 2015 May;157(5):271-84. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvv027. Epub 2015 Mar 13. J Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25770121 Review.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor in physiology and infectious diseases.Cytokine. 2017 Oct;98:97-106. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.12.025. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Cytokine. 2017. PMID: 28094206 Review.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor as mitogen, motogen and morphogen, and its roles in organ regeneration.Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994;24:195-213. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994. PMID: 8983076 Review.
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of HGF/Met in the cardiovascular system.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015 Dec;129(12):1173-93. doi: 10.1042/CS20150502. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26561593 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological roles of hepatocyte growth factor-Met signaling from genetically modified animals.Biomed Rep. 2017 Dec;7(6):495-503. doi: 10.3892/br.2017.1001. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Biomed Rep. 2017. PMID: 29188052 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Vascular Phenotypic and Proteomic Analysis in an Open Microfluidic Platform.ACS Nano. 2024 Sep 10;18(36):24909-24928. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c05537. Epub 2024 Aug 29. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 39208278 Free PMC article.
-
Interventional Potential of Recombinant Feline Hepatocyte Growth Factor in a Mouse Model of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Jul 23;9:378. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00378. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30083132 Free PMC article.
-
A case report of acute hepatic and renal failure associated with savolitinib treatment in advanced lung adenocarcinoma.AME Case Rep. 2025 Mar 7;9:51. doi: 10.21037/acr-24-156. eCollection 2025. AME Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40330941 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of esophageal epithelial regeneration following repair of surgical defects with acellular silk fibroin grafts.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 29;11(1):7086. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86511-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33782465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miyazawa K., Tsubouchi H., Naka D., Takahashi K., Okigaki M., Arakaki N., Nakayama H., Hirono S., Sakiyama O., Takahashi K., et al. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human hepatocyte growth factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989;163:967–973. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(89)92316-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

