Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia cells devoid of BTKC481S or CXCR4WHIM-like mutations acquire resistance to ibrutinib through upregulation of Bcl-2 and AKT resulting in vulnerability towards venetoclax or MK2206 treatment
- PMID: 28548645
- PMCID: PMC5518884
- DOI: 10.1038/bcj.2017.40
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia cells devoid of BTKC481S or CXCR4WHIM-like mutations acquire resistance to ibrutinib through upregulation of Bcl-2 and AKT resulting in vulnerability towards venetoclax or MK2206 treatment
Abstract
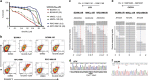
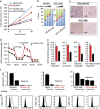
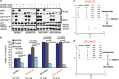
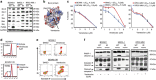
Although ibrutinib is highly effective in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (WM), no complete remissions in WM patients treated with ibrutinib have been reported to date. Moreover, ibrutinib-resistant disease is being steadily reported and is associated with dismal clinical outcome (overall survival of 2.9-3.1 months). To understand mechanisms of ibrutinib resistance in WM, we established ibrutinib-resistant in vitro models using validated WM cell lines. Characterization of these models revealed the absence of BTKC481S and CXCR4WHIM-like mutations. BTK-mediated signaling was found to be highly attenuated accompanied by a shift in PI3K/AKT and apoptosis regulation-associated genes/proteins. Cytotoxicity studies using the AKT inhibitor, MK2206±ibrutinib, and the Bcl-2-specific inhibitor, venetoclax±ibrutinib, demonstrated synergistic loss of cell viability when either MK22016 or venetoclax were used in combination with ibrutinib. Our findings demonstrate that induction of ibrutinib resistance in WM cells can arise independent of BTKC481S and CXCR4WHIM-like mutations and sustained pressure from ibrutinib appears to activate compensatory AKT signaling as well as reshuffling of Bcl-2 family proteins for maintenance of cell survival. Combination treatment demonstrated greater (and synergistic) antitumor effect and provides rationale for development of therapeutic strategies encompassing venetoclax+ibrutinib or PI3K/AKT inhibitors+ibrutinib in ibrutinib-resistant WM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Owen RG, Treon SP, Al-Katib A, Fonseca R, Greipp PR, McMaster ML et al. Clinicopathological definition of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia: consensus panel recommendations from the Second International Workshop on Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. Semin Oncol 2003; 30: 110–115. - PubMed
-
- Treon SP, Tripsas CK, Meid K, Warren D, Varma G, Green R et al. Ibrutinib in previously treated Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 1430–1440. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Hunter ZR, Liu X, Xu L, Yang G, Chen J et al. The WHIM-like CXCR4(S338X) somatic mutation activates AKT and ERK, and promotes resistance to ibrutinib and other agents used in the treatment of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. Leukemia 2015; 29: 169–176. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

