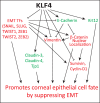
KLF4 Plays an Essential Role in Corneal Epithelial Homeostasis by Promoting Epithelial Cell Fate and Suppressing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
- PMID: 28549095
- PMCID: PMC5455171
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.17-21826
KLF4 Plays an Essential Role in Corneal Epithelial Homeostasis by Promoting Epithelial Cell Fate and Suppressing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to test the hypothesis that KLF4 promotes corneal epithelial (CE) cell fate by suppressing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), using spatiotemporally regulated CE-specific ablation of Klf4 in Klf4Δ/ΔCE (Klf4LoxP/LoxP/Krt12rtTA/rtTA/Tet-O-Cre) mice.
Methods: CE-specific ablation of Klf4 was achieved by feeding Klf4Δ/ΔCE mice with doxycycline chow. The wild-type (WT; normal chow-fed littermates) and the Klf4Δ/ΔCE histology was compared by hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections; EMT marker expression was quantified by quantitative PCR, immunoblots, and immunofluorescent staining; and wound healing rate was measured by CE debridement using Algerbrush. KLF4 and EMT markers were quantified in human corneal limbal epithelial (HCLE) cells undergoing TGF-β1-induced EMT by quantitative PCR, immunoblots, and immunofluorescent staining.
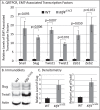
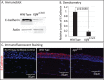
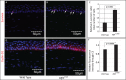
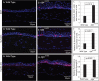
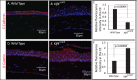
Results: The epithelial markers E-cadherin, Krt12, claudin-3, and claudin-4 were down-regulated, whereas the mesenchymal markers vimentin, β-catenin, survivin, and cyclin-D1 and the EMT transcription factors Snail, Slug, Twist1, Twist2, Zeb1, and Zeb2 were up-regulated in the Klf4Δ/ΔCE corneas. The Klf4Δ/ΔCE cells migrated faster, filling 93% of the debrided area within 16 hours compared with 61% in the WT. After 7 days of wounding, the Klf4Δ/ΔCE cells that filled the gap failed to regain epithelial characteristics, as they displayed abnormal stratification; down-regulation of E-cadherin and Krt12; up-regulation of β-catenin, survivin, and cyclin-D1; and a 2.5-fold increase in the number of proliferative Ki67+ cells. WT CE cells at the migrating edge and the HCLE cells undergoing TGF-β1-induced EMT displayed significant down-regulation of KLF4.
Conclusions: Collectively, these results reveal that KLF4 plays an essential role in CE homeostasis by promoting epithelial cell fate and suppressing EMT.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Spatiotemporally Controlled Ablation of Klf5 Results in Dysregulated Epithelial Homeostasis in Adult Mouse Corneas.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Sep 1;58(11):4683-4693. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22498. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28910443 Free PMC article.
-
KLF4 Regulates Corneal Epithelial Cell Cycle Progression by Suppressing Canonical TGF-β Signaling and Upregulating CDK Inhibitors P16 and P27.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 Feb 1;60(2):731-740. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-26423. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 30786277 Free PMC article.
-
KLF4 Coordinates Corneal Epithelial Apical-Basal Polarity and Plane of Cell Division and Is Downregulated in Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 May 11;61(5):15. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.5.15. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32396634 Free PMC article.
-
Is the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition clinically relevant for the cancer patient?Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011 Nov;12(11):1891-9. doi: 10.2174/138920111798377021. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21470129 Review.
-
Regulation of EMT by KLF4 in gastrointestinal cancer.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013 Nov;13(9):986-95. doi: 10.2174/15680096113136660104. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 24168184 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Conjunctival goblet cells: Ocular surface functions, disorders that affect them, and the potential for their regeneration.Ocul Surf. 2020 Jan;18(1):19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2019.11.005. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Ocul Surf. 2020. PMID: 31734511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corneal Epithelial Cells Exhibit Myeloid Characteristics and Present Antigen via MHC Class II.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Mar 1;59(3):1512-1522. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-23279. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29625473 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular nature of ocular surface barrier function, diseases that affect it, and its relevance for ocular drug delivery.Ocul Surf. 2023 Oct;30:3-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2023.08.001. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Ocul Surf. 2023. PMID: 37543173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of the regulatory circuit governing corneal epithelial fate determination and disease.PLoS Biol. 2023 Oct 19;21(10):e3002336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002336. eCollection 2023 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37856539 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporally Controlled Ablation of Klf5 Results in Dysregulated Epithelial Homeostasis in Adult Mouse Corneas.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Sep 1;58(11):4683-4693. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22498. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28910443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thiery JP,, Sleeman JP. Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006; 7: 131–142. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

