The Impact of Fatigue on Satisfaction of Search in Chest Radiography
- PMID: 28549868
- PMCID: PMC5557668
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2017.03.021
The Impact of Fatigue on Satisfaction of Search in Chest Radiography
Abstract
Rationale and objectives: To assess the nature of the satisfaction of search (SOS) effect in chest radiography when observers are fatigued; determine if we could replicate recent findings that have documented the nature of the SOS effect to be due to a threshold shift rather than a change in diagnostic accuracy as in earlier film-based studies.
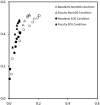
Materials and methods: Nearing or at the end of a clinical workday, 20 radiologists read 64 chest images twice, once with and once without the addition of a simulated pulmonary nodule. Half of the images had different types of "test" abnormalities. Decision thresholds were analyzed using the center of the range of false-positive (FP) and true-positive (TP) fractions associated with each receiver operating characteristic (ROC) point for reporting test abnormalities. Detection accuracy was assessed with ROC technique and inspection time was recorded.
Results: The SOS effect was confirmed to be a reduction in willingness to respond (threshold shift). The center of the FP range was significantly reduced (FP = 0.10 without added nodules, FP = 0.05 with added nodules, F(1,18) = 19.85, P = 0.0003). The center of the TP range was significantly reduced (TP = 0.39 without added nodules, TP = 0.33 with added nodules, F(1,18) = 10.81, P = 0.004).
Conclusions: This study suggests that fatigue does not change the nature of the SOS effect, but rather may be additive with the SOS effect. SOS reduces both TP and FP responses, whereas fatigue reduces TPs more than FPs.
Keywords: Satisfaction of search; accuracy; fatigue; performance.
Copyright © 2017 The Association of University Radiologists. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflict of interests to report
Figures

Similar articles
-
Satisfaction of Search in Chest Radiography 2015.Acad Radiol. 2015 Nov;22(11):1457-65. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2015.07.011. Epub 2015 Sep 9. Acad Radiol. 2015. PMID: 26363824 Free PMC article.
-
Reporting instructions significantly impact false positive rates when reading chest radiographs.Eur Radiol. 2016 Oct;26(10):3654-9. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-4194-1. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Eur Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26780639
-
The Influence of a Vocalized Checklist on Detection of Multiple Abnormalities in Chest Radiography.Acad Radiol. 2016 Apr;23(4):413-20. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2015.12.017. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Acad Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26916249
-
Does computer-aided diagnosis for lung tumors change satisfaction of search in chest radiography?Acad Radiol. 2007 Sep;14(9):1069-76. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2007.06.001. Acad Radiol. 2007. PMID: 17707314 Free PMC article.
-
Role of faulty decision making in the satisfaction of search effect in chest radiography.Acad Radiol. 2000 Dec;7(12):1098-106. doi: 10.1016/s1076-6332(00)80063-x. Acad Radiol. 2000. PMID: 11131054
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Technology-Supported Ultrasound Training in Prenatal Diagnosis through an Adaptive Image Recognition Training System (AdaptUS).Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2025 Mar 5;85(3):323-332. doi: 10.1055/a-2510-7185. eCollection 2025 Mar. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2025. PMID: 40052014 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding public perception of health examination services: Key factors influencing satisfaction in Türkiye.PLoS One. 2025 May 29;20(5):e0324125. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324125. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40440609 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Fatigue From Overnight Shifts on Radiology Search Patterns and Diagnostic Performance.J Am Coll Radiol. 2018 Dec;15(12):1709-1716. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2017.12.019. Epub 2018 Feb 1. J Am Coll Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29366599 Free PMC article.
-
From "satisfaction of search" to "subsequent search misses": a review of multiple-target search errors across radiology and cognitive science.Cogn Res Princ Implic. 2021 Aug 28;6(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s41235-021-00318-w. Cogn Res Princ Implic. 2021. PMID: 34455466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of fatigue on reading computed tomography examination of the multiply injured patient.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2017 Jul;4(3):035504. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.4.3.035504. Epub 2017 Sep 29. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2017. PMID: 28983495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kohn LT, Corrigan JM, Donaldson MS, editors. To Err is Human: Building a Safer Health System. National Academy Press; Washington, DC: 1999. - PubMed
-
- Bleich S. (Commonwealth Fund Publication #830).Medical Errors: Five years after the IOM report. 2005 Jul; http://www.commonwealthfund.org/usr_doc/830_Bleich_errors.pdf Last accessed July 13, 2016. - PubMed
-
- O’Donnell EP, Humeniuk KM, West CP, Tiburt JC. The effects of fatigue and dissatisfaction on how physicians perceive their social responsibilities. Mayo Clin Proc. 2015;90:194–201. - PubMed
-
- Chan AOM, Chan YH, Chuang KP, Ng JSC, Neo PSH. Addressing physician quality of life: understanding the relationship between burnout, work engagement, compassion fatigue and satisfaction. J Hosp Admin. 2015;4:46–55.
-
- Bruno MA, Walker EA, Abujudeh HH. Understanding and confronting our mistakes: the epidemiology of error in radiology and strategies for error reduction. RadioGraphics. 2015;35:1668–1676. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

