Early transcriptome responses of the bovine midcycle corpus luteum to prostaglandin F2α includes cytokine signaling
- PMID: 28549990
- PMCID: PMC7388008
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.05.018
Early transcriptome responses of the bovine midcycle corpus luteum to prostaglandin F2α includes cytokine signaling
Abstract
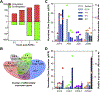
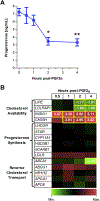
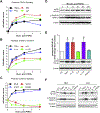
In ruminants, prostaglandin F2alpha (PGF2α)-mediated luteolysis is essential prior to estrous cycle resumption, and is a target for improving fertility. To deduce early PGF2α-provoked changes in the corpus luteum a short time-course (0.5-4 h) was performed on cows at midcycle. A microarray-determined transcriptome was established and examined by bioinformatic pathway analysis. Classic PGF2α effects were evident by changes in early response genes (FOS, JUN, ATF3) and prediction of active pathways (PKC, MAPK). Several cytokine transcripts were elevated and NF-κB and STAT activation were predicted by pathway analysis. Self-organizing map analysis grouped differentially expressed transcripts into ten mRNA expression patterns indicative of temporal signaling cascades. Comparison with two analogous datasets revealed a conserved group of 124 transcripts similarly altered by PGF2α treatment, which both, directly and indirectly, indicated cytokine activation. Elevated levels of cytokine transcripts after PGF2α and predicted activation of cytokine pathways implicate inflammatory reactions early in PGF2α-mediated luteolysis.
Keywords: Corpus luteum; Cytokine; Luteolysis; PGF2α; Regression; Signaling.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Acosta TJ, Yoshizawa N, Ohtani M, Miyamoto A, 2002. Local changes in blood flow within the early and midcycle corpus luteum after prostaglandin F(2 alpha) injection in the cow. Biol. Reprod 66, 651–658. - PubMed
-
- Arvisais E, Hou X, Wyatt TA, Shirasuna K, Bollwein H, Miyamoto A, Hansen TR, Rueda BR, Davis JS, 2010. Prostaglandin F2alpha represses IGF-I-stimulated IRS1/phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/AKT signaling in the corpus luteum: role of ERK and P70 ribosomal S6 kinase. Mol. Endocrinol. 24, 632–643. 10.1210/me.2009-0312. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

