Efficacy of rasagiline and selegiline in Parkinson's disease: a head-to-head 3-year retrospective case-control study
- PMID: 28550482
- PMCID: PMC5570795
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-017-8523-y
Efficacy of rasagiline and selegiline in Parkinson's disease: a head-to-head 3-year retrospective case-control study
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Efficacy of rasagiline and selegiline in Parkinson's disease: a head-to-head 3-year retrospective case-control study.J Neurol. 2017 Sep;264(9):2051. doi: 10.1007/s00415-017-8585-x. J Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28831499 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
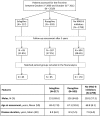
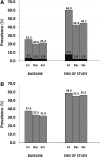
Monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) inhibitors, such as selegiline and rasagiline, can be used as monotherapy or adjuvant therapy to levodopa in Parkinson's disease (PD). Data on long-term efficacy of MAO-B inhibitors are limited with no head-to-head comparison available to date. The aim of this case-control retrospective study was to analyze data from patients with PD attending the Parkinson Institute (Milan, Italy) over a 6-year period (2009-2015) and compare the effects of selegiline and rasagiline on levodopa treatment outcomes. Patients with PD treated with either selegiline (n = 85) or rasagiline (n = 85) for 3 years as well as a control group of patients (N = 170) who have never received MAO-B inhibitors, were matched for gender, disease duration (±1 year) and age (±1 year) at baseline assessment (ratio 1:1:2). The Unified PD Rating Scale and the Hoehn-Yahr staging system were used for clinical comparisons. At baseline, mean PD duration was 6.5 years and clinical features were comparable across all three groups. After a mean follow-up of approximately 37 months, no differences in clinical progression of motor and non-motor symptoms were observed between the three groups. However, MAO-B inhibitor use was associated with ~2-fold lower change in daily dose of levodopa (p < 0.001) and lower dyskinesia scores (p = 0.028) than non-users. No intra-class differences were observed between selegiline and rasagiline. Long-term use of MAO-B inhibitors resulted in a significant reduction in levodopa requirements and a lower frequency of dyskinesias in patients with PD. Selegiline and rasagiline had equal efficacy in controlling motor symptoms in PD patients on optimized therapy.
Keywords: Levodopa; Monoamine oxidase inhibitors; Parkinson’s disease; Rasagiline; Selegiline.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
This work was supported by the Fondazione Grigioni per il Morbo di Parkinson.
Ethical standards
This study was performed in agreement with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and the local Ethics Committee was notified in compliance with Italian legislation on retrospective studies. For every patient included, the written informed consent previously signed to allow the use of clinical data for research purposes was retrieved.
Conflicts of interest
The authors certify that over the last 3 years there were no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with a direct financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed herein. Dr. Cilia received honoraria for symposia from Boehringer-Ingelheim, Lundbeck, UCB pharma. Emanuele Cereda has received consultancy honoraria and investigator grants from the Fondazione Grigioni per il Morbo di Parkinson, the Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo and Nutricia Italia.
Figures
References
-
- Schatz IJ, et al. Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, pure autonomic failure, and multiple system atrophy. The Consensus Committee of the American Autonomic Society and the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 1996;46:1470. doi: 10.1212/WNL.46.5.1470. - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, fourth edition, text revision. New York: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
-
- Cilia R, Cereda E, Amboni M, Akpalu A, Sarfo FS, Cham M, Fabbri M, Pezzoli G (2016) Long-duration response to levodopa in Parkinson’s disease is independent of disease duration: A prospective study on de novo patients in Ghana (abstract). In: 20th International Congress of the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society. Mov Disord, Berlin, Germany
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

