Prion-Like Seeding of Misfolded α-Synuclein in the Brains of Dementia with Lewy Body Patients in RT-QUIC
- PMID: 28550528
- PMCID: PMC5884914
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-017-0624-1
Prion-Like Seeding of Misfolded α-Synuclein in the Brains of Dementia with Lewy Body Patients in RT-QUIC
Abstract
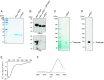
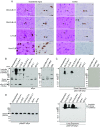
The prion-like seeding of misfolded α-synuclein (αSyn) involved in the pathogenesis of Lewy body diseases (LBD) remains poorly understood at the molecular level. Using the real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QUIC) seeding assay, we investigated whether brain tissues from cases of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), which contain serine 129 (Ser129)-phosphorylated insoluble aggregates of αSyn, can convert Escherichia coli-derived recombinant αSyn (r-αSyn) to fibrils. Diffuse neocortical DLB yielded 50% seeding dose (SD50) values of 107~1010/g brain. Limbic DLB was estimated to have an SD50 value of ~105/g brain. Furthermore, RT-QUIC assay discriminated DLB from other neurological and neurodegenerative disorders. Unexpectedly, the prion-like seeding was reconstructed in reactions seeded with oligomer-like species, but not with insoluble aggregates of r-αSyn, regardless of Ser129 phosphorylation status. Our findings suggest that RT-QUIC using r-αSyn can be applied to detect seeding activity in LBD, and the culprit that causes prion-like seeding may be oligomeric forms of αSyn.
Keywords: Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB); Prion; Real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QUIC); α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

