Brevetoxin-2, is a unique inhibitor of the C-terminal redox center of mammalian thioredoxin reductase-1
- PMID: 28551108
- PMCID: PMC5623065
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.05.027
Brevetoxin-2, is a unique inhibitor of the C-terminal redox center of mammalian thioredoxin reductase-1
Abstract
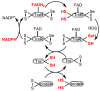
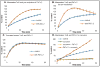
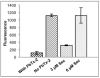
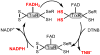
Karenia brevis, the Florida red tide dinoflagellate produces a suite of neurotoxins known as the brevetoxins. The most abundant of the brevetoxins PbTx-2, was found to inhibit the thioredoxin-thioredoxin reductase system, whereas the PbTx-3 has no effect on this system. On the other hand, PbTx-2 activates the reduction of small disulfides such as 5,5'-dithio-bis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) by thioredoxin reductase. PbTx-2 has an α, β-unsaturated aldehyde moiety which functions as an efficient electrophile and selenocysteine conjugates are readily formed. PbTx-2 blocks the inhibition of TrxR by the inhibitor curcumin, whereas curcumin blocks PbTx-2 activation of TrxR. It is proposed that the mechanism of inhibition of thioredoxin reduction is via the formation of a Michael adduct between selenocysteine and the α, β-unsaturated aldehyde moiety of PbTx-2. PbTx-2 had no effect on the rates of reactions catalyzed by related enzymes such as glutathione reductase, glutathione peroxidase or glutaredoxin.
Keywords: Brevetoxin; Karenia brevis; Thioredoxin; Thioredoxin reductase.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


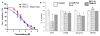
Similar articles
-
Brevetoxin (PbTx-2) influences the redox status and NPQ of Karenia brevis by way of thioredoxin reductase.Harmful Algae. 2018 Jan;71:29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2017.11.004. Harmful Algae. 2018. PMID: 29306394 Free PMC article.
-
The Marine Neurotoxin Brevetoxin (PbTx-2) Inhibits Karenia brevis and Mammalian Thioredoxin Reductases by Targeting Different Residues.J Nat Prod. 2021 Nov 26;84(11):2961-2970. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c00795. Epub 2021 Nov 9. J Nat Prod. 2021. PMID: 34752085
-
Characterization of brevetoxin (PbTx-3) exposure in neurons of the anoxia-tolerant freshwater turtle (Trachemys scripta).Aquat Toxicol. 2016 Nov;180:115-122. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.09.016. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Aquat Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27697698
-
The thioredoxin antioxidant system.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Jan;66:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.036. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 23899494 Review.
-
Thioredoxin Reductase Inhibition for Cancer Therapy.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022 Jan 6;62:177-196. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-052220-102509. Epub 2021 Aug 24. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 34449246 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectors of thioredoxin reductase: Brevetoxins and manumycin-A.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2019 Mar;217:76-86. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2018.11.015. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30476593 Free PMC article.
-
Brevetoxin (PbTx-2) influences the redox status and NPQ of Karenia brevis by way of thioredoxin reductase.Harmful Algae. 2018 Jan;71:29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2017.11.004. Harmful Algae. 2018. PMID: 29306394 Free PMC article.
-
Essential components of the xanthophyll cycle differ in high and low toxin Karenia brevis.Harmful Algae. 2021 Mar;103:102006. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2021.102006. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Harmful Algae. 2021. PMID: 33980446 Free PMC article.
-
Karenia brevis Extract Induces Cellular Entry through Distinct Mechanisms in Phagocytic RAW 264.7 Macrophages versus Non-Phagocytic Vero Cells.Mar Drugs. 2023 Dec 19;22(1):4. doi: 10.3390/md22010004. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 38276642 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Insights into Brevetoxicosis in Sea Turtles.Animals (Basel). 2024 Mar 22;14(7):991. doi: 10.3390/ani14070991. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38612230 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Flewelling LJ, Naar JP, Abbott JP, Baden DG, Barros NB, Bossart GD, Bottein M-YD, Hammond DG, Haubold EM, Heil CA, Henry MS, Jacocks HM, Leighfield TA, Pierce RH, Pitchford TD, Rommel SA, Scott PS, Steidinger KA, Truby EW, Van Dolah FM, Landsberg JH. Brevetoxicosis: Red tides and marine mammal mortalities. Nature. 2005;435:755–756. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bossart GD, Baden DG, Ewing RY, Roberts B, Wright SD. Brevetoxicosis in manatees (Trichechus manatus latirostris) from the 1996 epizootic: gross, histologic, and immunohistochemical features. Toxicol Pathol. 1998;26:276–282. - PubMed
-
- Fire SE, Flewelling LJ, Stolen M, Noke Durden W, de Wit M, Spellman AC, Wang Z. Brevetoxin-associated mass mortality event of bottlenose dolphins and manatees along the east coast of Florida, USA. Mar Ecol: Prog Ser. 2015;526:241–251.
-
- Fleming LE, Kirkpatrick B, Backer LC, Bean JA, Wanner A, Dalpra D, Tamer R, Zaias J, Cheng YS, Pierce R, Naar J, Abraham W, Clark R, Zhou Y, Henry MS, Johnson D, Van De Bogart G, Bossart GD, Harrington M, Baden DG. Initial evaluation of the effects of aerosolized Florida red tide toxins (brevetoxins) in persons with asthma. Environ Health Perspect. 2005;113:650–657. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

