The role of the ATP2C1 gene in Hailey-Hailey disease
- PMID: 28551824
- PMCID: PMC11107712
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-017-2544-7
The role of the ATP2C1 gene in Hailey-Hailey disease
Abstract
Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD) is a rare autosomal dominant acantholytic dermatosis, characterized by a chronic course of repeated and exacerbated skin lesions in friction regions. The pathogenic gene of HHD was reported to be the ATPase calcium-transporting type 2C member 1 gene (ATP2C1) located on chromosome 3q21-q24. Its function is to maintain normal intracellular concentrations of Ca2+/Mn2+ by transporting Ca2+/Mn2+ into the Golgi apparatus. ATP2C1 gene mutations are reportedly responsible for abnormal cytosolic Ca2+/Mn2+ levels and the clinical manifestations of HHD. Environmental factors and genetic modifiers may also affect the clinical variability of HHD. This article aims to critically discuss the clinical and pathological features of HHD, differential diagnoses, and genetic and functional studies of the ATP2C1 gene in HHD. Further understanding the role of the ATP2C1 gene in the pathogenesis of HHD by genetic, molecular, and animal studies may contribute to a better clinical diagnosis and provide new strategies for the treatment and prevention of HHD.
Keywords: Animal model; Clinical manifestation; Gene function; Genetics; Mutation analysis; Pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

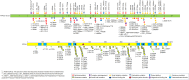
References
-
- Hailey H, Hailey H. Familial benign chronic pemphigus. Report of 13 cases in 4 generations of a family and report of 9 additional cases in 4 generations of a family. Arch Dermatol Syphilol. 1939;39:679–685. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1939.01480220064005. - DOI
-
- Raiko L, Siljamäki E, Mahoney MG, Putaala H, Suominen E, Peltonen J, Peltonen S. Hailey–Hailey disease and tight junctions: claudins 1 and 4 are regulated by ATP2C1 gene encoding Ca2+/Mn2+ ATPase SPCA1 in cultured keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 2012;21:586–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2012.01520.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2016YFC1306604/National Key Research and Development Program of China/International
- 81670216/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 2015JJ4088/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province/International
- 2016JJ2166/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province/International
- 20150301/New Xiangya Talent Project of the Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

