The autonomic medical history
- PMID: 28551871
- PMCID: PMC8942132
- DOI: 10.1007/s10286-017-0425-7
The autonomic medical history
Abstract
The most important autonomic function test-the autonomic medical history-is the patient's account, interpreted by a clinician skilled in asking the right questions, of symptoms during daily activities that relate to the autonomic nervous system. The chronology and pattern of these symptoms combine to create a portrait of autonomic function or dysfunction. We summarize the steps in obtaining a comprehensive autonomic medical history.
Keywords: Autonomic; Cholinergic; Noradrenergic; Parasympathetic; Sympathetic.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

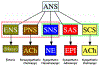
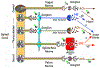
Comment in
-
The most accurate autonomic function test: the medical history.Clin Auton Res. 2017 Aug;27(4):209-210. doi: 10.1007/s10286-017-0449-z. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Clin Auton Res. 2017. PMID: 28710603 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cannon WB (1919) Bodily Changes in Pain, Hunger, Fear and Rage. D. Appleton & Co., New York
-
- Cheshire WP Syncope. Continuum; (in press) - PubMed
-
- Cheshire WP (2016) Stimulant medication and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: a tale of two cases. Clin. Auton. Res 26:229–233 - PubMed
-
- Cheshire WP, Fealey RD (2008) Drug-induced hyperhidrosis and hypohidrosis: incidence, prevention and management. Drug Saf. 31:109–126 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

