Whole-Genome Sequencing Coupled to Imputation Discovers Genetic Signals for Anthropometric Traits
- PMID: 28552196
- PMCID: PMC5473732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.04.014
Whole-Genome Sequencing Coupled to Imputation Discovers Genetic Signals for Anthropometric Traits
Abstract
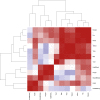
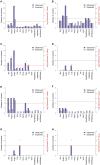
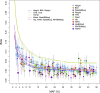
Deep sequence-based imputation can enhance the discovery power of genome-wide association studies by assessing previously unexplored variation across the common- and low-frequency spectra. We applied a hybrid whole-genome sequencing (WGS) and deep imputation approach to examine the broader allelic architecture of 12 anthropometric traits associated with height, body mass, and fat distribution in up to 267,616 individuals. We report 106 genome-wide significant signals that have not been previously identified, including 9 low-frequency variants pointing to functional candidates. Of the 106 signals, 6 are in genomic regions that have not been implicated with related traits before, 28 are independent signals at previously reported regions, and 72 represent previously reported signals for a different anthropometric trait. 71% of signals reside within genes and fine mapping resolves 23 signals to one or two likely causal variants. We confirm genetic overlap between human monogenic and polygenic anthropometric traits and find signal enrichment in cis expression QTLs in relevant tissues. Our results highlight the potential of WGS strategies to enhance biologically relevant discoveries across the frequency spectrum.
Keywords: DXA traits; UK Biobank; UK10K; anthropometry; genetic association study; imputation; next-generation whole-genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Haslam D.W., James W.P. Obesity. Lancet. 2005;366:1197–1209. - PubMed
-
- Barness L.A., Opitz J.M., Gilbert-Barness E. Obesity: genetic, molecular, and environmental aspects. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2007;143A:3016–3034. - PubMed
-
- Locke A.E., Kahali B., Berndt S.I., Justice A.E., Pers T.H., Day F.R., Powell C., Vedantam S., Buchkovich M.L., Yang J., LifeLines Cohort Study. ADIPOGen Consortium. AGEN-BMI Working Group. CARDIOGRAMplusC4D Consortium. CKDGen Consortium. GLGC. ICBP. MAGIC Investigators. MuTHER Consortium. MIGen Consortium. PAGE Consortium. ReproGen Consortium. GENIE Consortium. International Endogene Consortium Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature. 2015;518:197–206. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shungin D., Winkler T.W., Croteau-Chonka D.C., Ferreira T., Locke A.E., Mägi R., Strawbridge R.J., Pers T.H., Fischer K., Justice A.E., ADIPOGen Consortium. CARDIOGRAMplusC4D Consortium. CKDGen Consortium. GEFOS Consortium. GENIE Consortium. GLGC. ICBP. International Endogene Consortium. LifeLines Cohort Study. MAGIC Investigators. MuTHER Consortium. PAGE Consortium. ReproGen Consortium New genetic loci link adipose and insulin biology to body fat distribution. Nature. 2015;518:187–196. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MR/K002414/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0900753/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N01104X/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N011317/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/08/014/24067/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 648916/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0902313/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/8/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 20308/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- MR/J012165/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/11/4/28734/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/N01104X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CZB/4/733/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12015/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K002279/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 202802/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0600237/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0100594/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0901461/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

